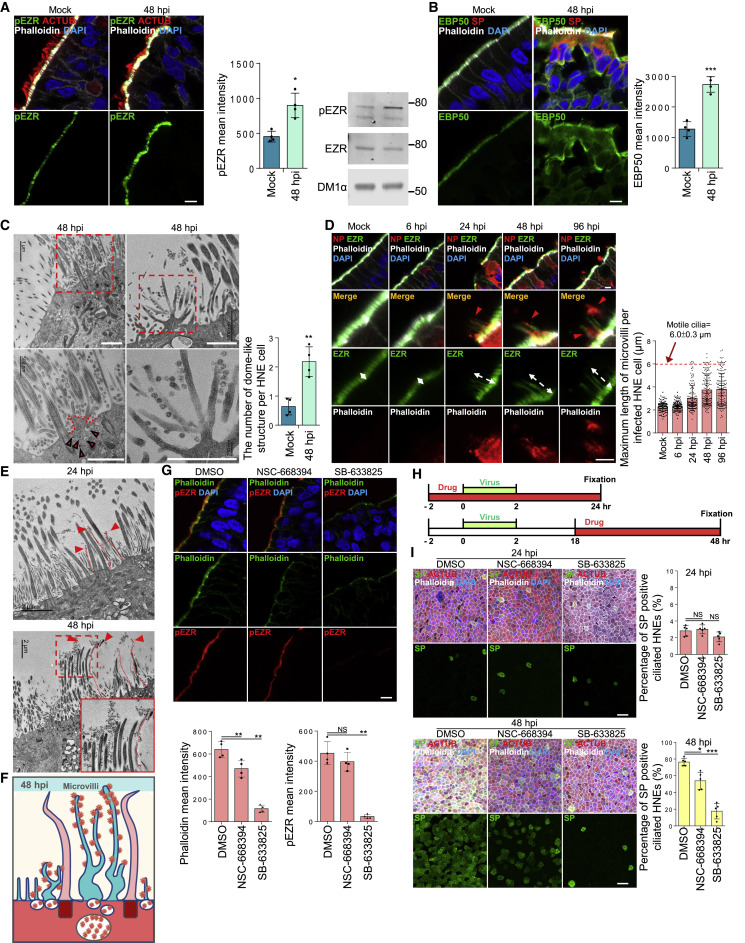
Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2 regulates the dynamics of microvilli and promotes highly extended microvilli to facilitate viral shedding/secretion
(A and B) SARS-CoV-2 infection increases phosphorylated ezrin (EZR) and EBP50 protein on microvilli.
(A) Mock-treated or infected HNEs (MOI 0.3) were stained 48 hpi. Representative IF staining of pEZR and phalloidin with ACTUB in mock or infected HNEs Donor 3 (left panel). Quantification of pEZR from mock and infected HNEs Donors 3–6 (middle panel). pEZR expression increased in SARS-CoV-2-infected HNEs compared to mock controls. pEZR and EZR immunoblots of in mock or infected HNEs Donor 6 (right panel). Donors 4 and5 showed similar results.
(B) Mock-treated or SARS-CoV-2-infected HNEs (MOI 0.3) were stained 48 hpi. Representative IF staining of EBP50, phalloidin and SARS-CoV-2 SP for mock versus infected HNEs (Donor 3). Quantification of EBP50 on microvilli from mock and infected HNEs Donor 3–6 (right panel). EBP50 expression increased in infected HNEs compared to mock controls.
(C–E) SARS-CoV-2 infection affects microvillar structure. (C and E) Infected HNEs (Donor 3) with MOI of 0.3 were fixed at 24 and 48 hpi. Cells were observed by TEM. (C) Quantification of the number of dome-shaped structures per cell from Donors 3–6 (right panel). Error bars represent mean ± SD (200 ciliated HNEs were counted from 4 donors each).
(A, B, and C) Error bars represent mean ± SD ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, NS represents not significant, paired, two-tailed Student’s t test. Red arrowhead: small viral vesicle.
(D) Mock-treated or infected HNEs with MOI of 0.3 were stained at 6, 24, 48, and 96 hpi. Representative IF staining of SARS-CoV-2 NP, EZR, and phalloidin in mock or SARS-CoV-2-infected HNEs from Donor 3 (right panel). Quantification of the length of EZR from mock and SARS-CoV-2-infected HNEs from Donors 3–550 ciliated HNEs from 4 donors each).
White dotted line: extended microvilli. Red arrowhead: virus particles (E) SARS-CoV-2 infection induce overly long microvilli attached with virus particles at 24 (upper image) and 48 (lower image) hpi. Red dotted line: extended microvilli.
(F) Model of microvilli structures and viral vesicles affected by SARS-Co-V2 infection.
(G) Microvillar inhibitors inhibit microvilli structure. Representative IF staining of pEZR and phalloidin in DMSO-, NSC-668394 (40 μM)-, and SB-633825 (40 μM)-treated HNEs from Donor 5 Quantification of pEZR and phalloidin from DMSO- or drug-treated HNEs (3 h treatment) Donors 5–8 (down panel). pEZR and phalloidin expression showed a decrease in drug-treated HNEs, compared to DMSO-treated cells.
(H) SARS-CoV-2-treated HNEs were treated with NSC-668394 or SB-633825 (see schematic).
(I) Microvilli inhibitors, NSC-668394 (40 μM) and SB-633825 (40 μM), significantly inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in HNEs. Representative IF staining of SARS-CoV-2 SP, ACTUB, and phalloidin in DMSO- or drug-treated SARS-CoV-2-infected HNEs at 24 hpi (upper image) and 48 hpi (down image) (Donor 5). Quantified percentages of SP-positive ciliated HNEs (right panel). Error bars represent mean ± SD (3,000–4,000 HNEs were quantified Donors 4–8).
(G and I) Error bars represent mean ± SD ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, NS represents not significant, paired, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. Each dot represents one donor. Scale bars: 5 μm (A, B, D, and G), 1 μm (C), 2 μm (E), 20 μm (I). See Figure S4 and Table S1.