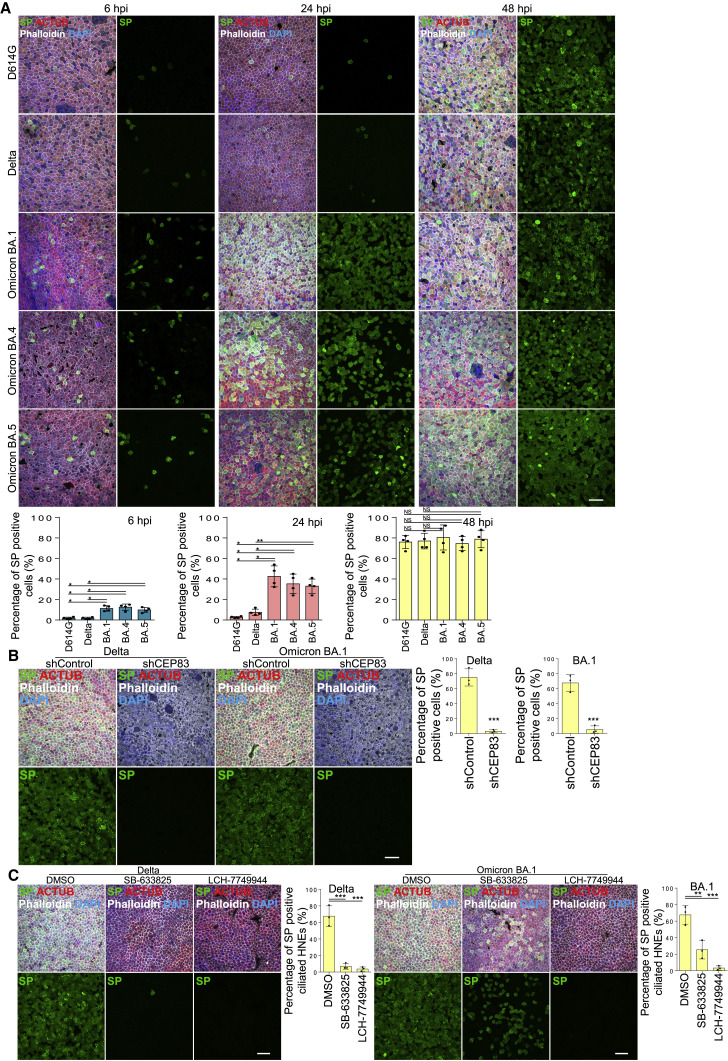
Figure 7.
Higher viral entry and replication of Omicron in human nasal epithelium
(A) Omicron variants show notable increase of infected cells at early timepoints. Mock-treated or SARS-CoV-2 D614G, Delta, and Omicron (BA.1, BA.4, BA.5) strain-infected HNEs (MOI 0.3) were stained at 6 (left), 24 (middle), and 48 hpi (right). Representative IF images of HNEs stained for SP, NP, and CED marker ACTUB. Quantified percentages of NP- and SP-positive ciliated nasal epithelial cells or goblet cells (right panel).
(B and C) Cilia and microvilli remain critical in Delta and Omicron infections. (B) SARS-CoV-2 variants infected HNEs (MOI 0.3) were stained 48 hpi. Representative IF staining for SP and ACTUB with phalloidin in shControl and shCEP83 Delta (left)- or Omicron BA.1 (right)-infected HNEs. Quantified percentages of SP-positive HNEs (right panel). Error bars represent mean ± SD (3,000–4,000 HNEs Donors 6–8).
(C) SARS-CoV-2 variant-treated HNEs were treated with SB-633825 (40 μM) and LCH-7749944 (20 μM) as in Figure 5H. Representative IF staining of SARS-CoV-2 SP, ACTUB, and phalloidin staining in DMSO- versus drug-treated Delta (left)- or Omicron BA.1 (right)-infected HNEs. Quantified percentages of SP-positive ciliated HNEs (right). Error bars represent mean ± SD (3,000–4,000 NHEs Donors 6–8). (A–C) ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test (A and C) or paired, two-tailed Student’s t test (B). Each dot = one donor. Scale bars represent 20 μm.