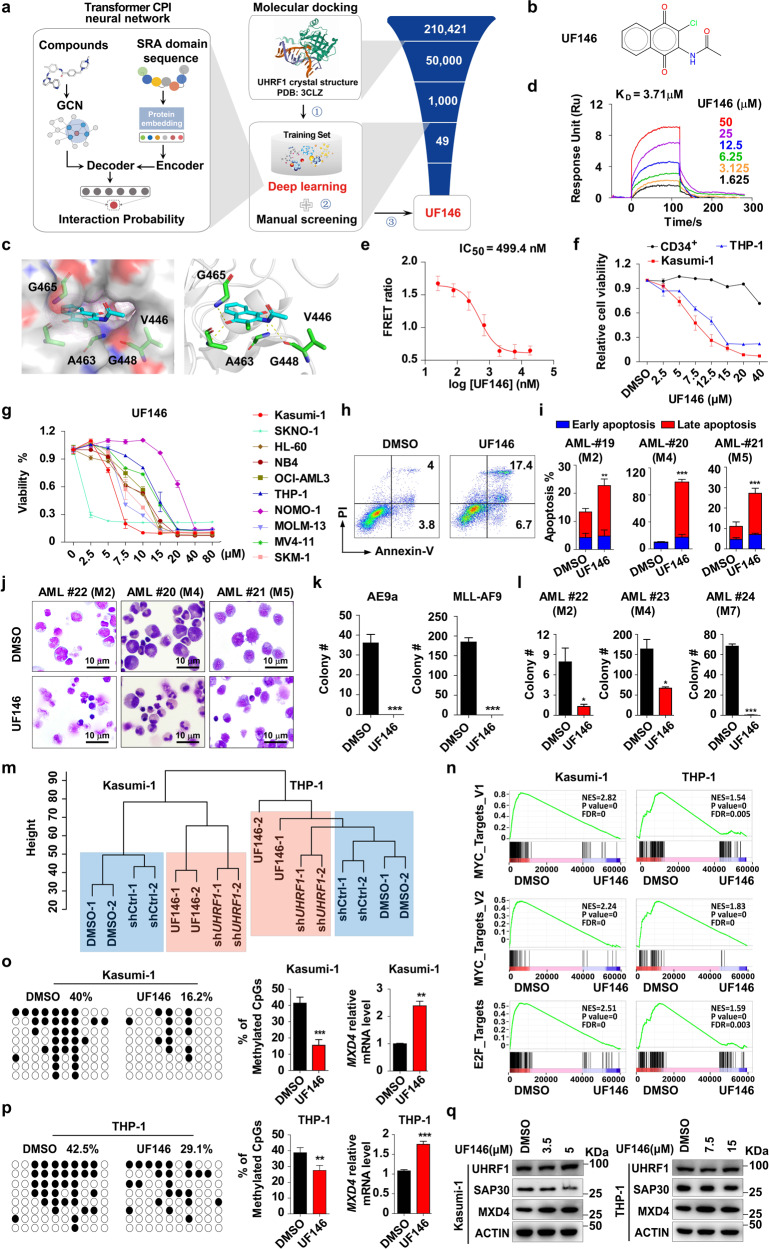
Fig. 7. UHRF1 inhibitor UF146 suppresses AML cell survival by inhibiting proliferation and promoting apoptosis in vitro.
a The scheme of the screening protocol for UHRF1 inhibitor. b The structural formula of UHRF1 inhibitor UF146. c The binding mode of UF146 to the G465, A463, G448 and V446-created 5mC cavity in SRA domain. d, e The SPR (d) and FRET (e) analysis were performed to examine the direct binding affinities of UF146 to the SRA domain of UHRF1 (n = 3). f The cellular viability of human CD34+ HSPCs, Kasumi-1 and THP-1 cells treated with UF146 or the vehicle was examined by MTT assay (n = 3). g The cellular viability of AML cells (Kasumi-1, SKNO-1, HL60, NB4, OCI-AML3, THP-1, NOMO-1, MOLM-13, MV4-11 and SKM-1 cells) treated with UF146 or the vehicle control for 48 h. h, i The representative flow cytometry analysis profiles (h) and quantification (i) analysis of the early apoptosis and late apoptosis in the primary AML patient cells 24 h after the treatment of UF146 or the vehicle control (n = 3). j The Wright’s staining of the primary AML cells treated with the vehicle or UF146. k The number of colonies generated from AE9a- or MLL-AF9-driven LICs treated with UF146 or the vehicle (n = 3). l The number of colonies generated from the primary AML patient cells treated with UF146 or the vehicle (n = 3). m The cluster dendrogram analysis of AML cells treated with UF146 and AML cells with knockdown of UHRF1. n The RNA-seq and GSEA analysis of the AML cells treated with UF146 or the vehicle. o, p The DNA methylation levels of MXD4 in UF146- or the vehicle-treated Kasumi-1 (o) and THP-1 (p) cells were analyzed by the bisulfite sequencing (n = 3). q Western blotting analysis of UHRF1/MXD4/SAP30 in AML cells 24 h after UF146 treatment. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s unpaired t-test for i, k, l, o and p. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.