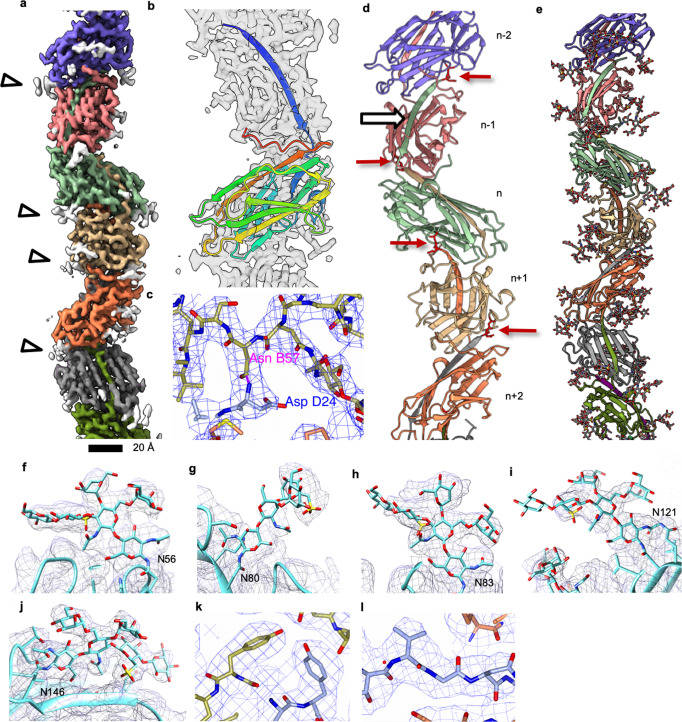
Fig. 1. Helical reconstruction and atomic model of the thread.
a Segmented surface representation of the cryoEM map showing each subunit in a different colour. Glycan densities are shown in white (white arrowheads). b The atomic model of one Saci_0406 subunit (rainbow) fitted into the cryoEM map (transparent grey) N-terminus, blue; C-terminus, red. Glycans not shown for simplicity. c Intermolecular isopeptide bond is shown as a dashed purple line. The N-terminal residue Asp24 of a subunit (n + 2; carbons in ice blue) appears to be covalently bound to Asn57 two subunits along the chain (n; carbons in gold). d Atomic model of 5 consecutive Saci_0406 subunits in ribbon representation. Glycans are not shown for simplicity. A white arrow indicates the location of the donor strand complementation between the N-terminal tail domain of subunit (n) and the C-terminal head domain of the previous subunit in the chain (n − 1). Red arrows indicate the location of isopeptide bonds. The tail domain of each subunit n is partially buried in the two consecutive subunits n − 1 and n − 2. e Atomic model of the thread filament with glycans in stick representation. f–j Closeups of the five glycosylation sites found in Saci_0406. Atomic models of the glycans are in stick, the polypeptide backbone in ribbon representation. The CryoEM density map is shown as grey mesh. k, l Closeups of map and fitted atomic model demonstrating the quality of the data. The colour scheme is as in C, chain (n-1) shows carbons in coral. Scale bar 20 Å.