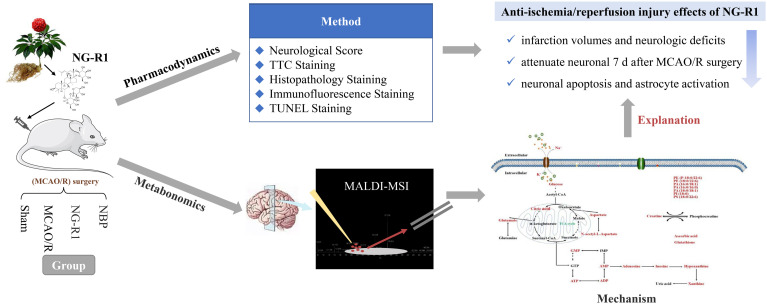
Fig. 4.
Spatially resolved metabolomics based on MSI to elucidate the pharmacodynamic mechanisms of NG-R1 (Zhu et al., 2020). The rats in this study were divided into four groups: Sham, MCAO/R, NG-R1 (20 mg/kg, 7 days), and NBP (20 mg/kg, 7 days). Pharmacodynamic studies (included neurological score, TTC staining, histopathology staining, immunofluorescence staining, and TUNEL staining) conducted 7 days after ischemic-reperfusion showed that NG-R1 can reduce infarction volumes and neurologic deficits in MCAO/R rats and attenuate neuronal loss 7 d after MCAO/R surgery, while also inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and astrocyte activation. To clarify the mechanisms by which those events occur, the study further used spatially resolved metabolomics based on MALDI-MSI and found that NG-R1 can regulate the abnormal accumulation of glucose and citric acid, increase the content of glutamate and malate-aspartic acid shuttle components, increase antioxidant content, increase ATP metabolism, and maintain the homeostasis of Na+ and K+ to achieve anti-ischemia/reperfusion injury effects.