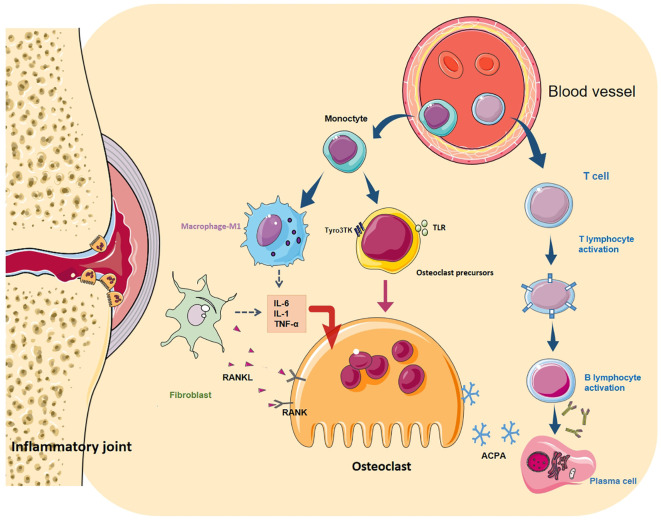
Figure 2.
Differentiation regulation of osteoclasts. OC differentiation is a multi-step process, in which cytokines and various cell interactions affect the differentiation of OC from the mononuclear to the terminal state. Among them, autoantibodies directly act on OCs (and their precursors) or cooperate with T and B cells to form a vicious circle. Toll-like receptors (TLR) and Tyro3TK on the surface of OCPs bind to their specific ligands to affect OC differentiation. M1 macrophages secrete many pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and various matrix lyases to activate OCs and aggravate the inflammatory reaction. FLS is the key cell in RA bone destruction. Various pro-inflammatory factors allow it to express RANKL in large quantities. It binds to RANK on the surface of macrophages and OCs and promotes the maturation of OCs through NF- κB signal cascade.