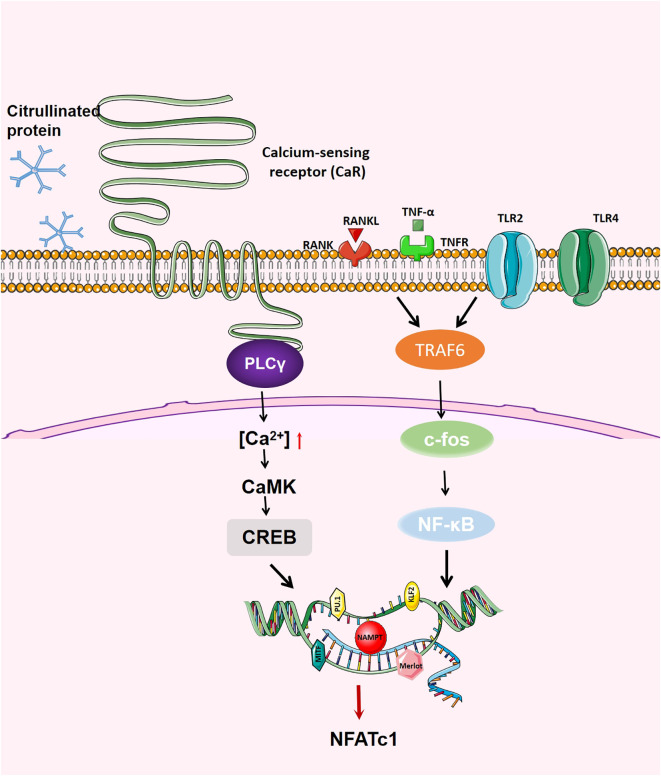
Figure 3.
Generation regulation of OCs. When RANK binds to RANKL, on the one hand, RANK recruits TRAF6, activates NF- κB, JNK,p38,c-fos and AP-1; on the other hand, RANK increases the activity of intracellular calcium and activates calcium regulatory neuroenzymes through the Btk/Tec pathway, which promotes the production of phospholipase C (PLC) to mediate the release of intracellular calcium, regulating the activity of CREB and affecting the transcription of various transcription factors.NFATc1 is the main transcription factor in OC differentiation, inducing OC-specific target genes in the nucleus.The activation of NFATc1 is induced by the above two pathways, thus promoting the formation of OC.