FIGURE 3.
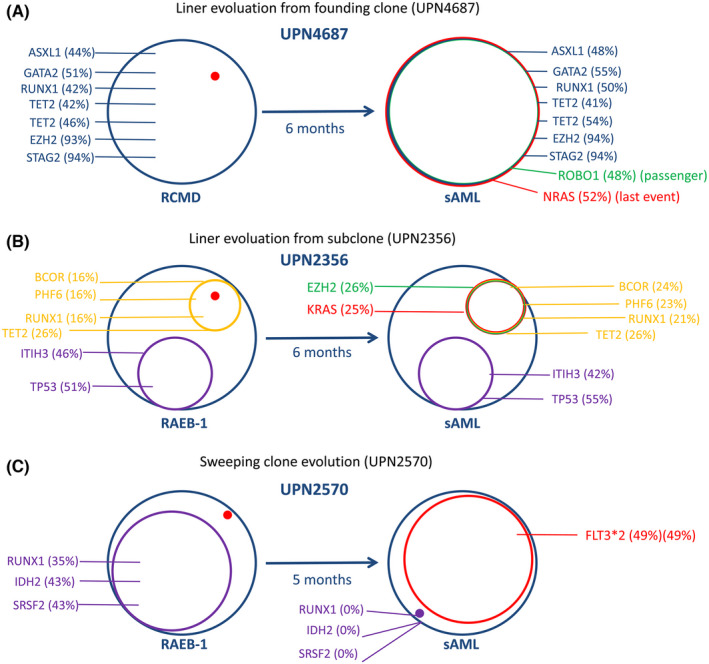
Three evolution patterns for AML transformation. (A). Linear evolution, based on the founding clone, is shown for UPN4687. Similar cases include UPN809, 1057, 3435, 3626, 1792, 3183, 1891, 1243, 3288, 1090, 1018, 3552, 3826, 4196, 4634, 1582, 1831, 2296, 843, 702, 3430, 3541, 2638, 4133, 4820, 4877, 5135 and 5305. (B). Linear evolution from a subclone is shown for UPN2356. Similar cases include UPN4603, 2577, 692, and 2666. Linear evolution includes two models (from founding clone and subclone). Red dots mean the origin of the red cycle (right graph). (C). Sweeping clone evolution is shown for UPN2570. Similar cases include UPN811, 1354, 3053, 3567 and 4383. [Number] indicates VAF; [H] indicates homozygous mutations; red indicates presumed the last mutation; green indicates newly emerged partner mutations, which could not be presumed to be AML TRMs.
