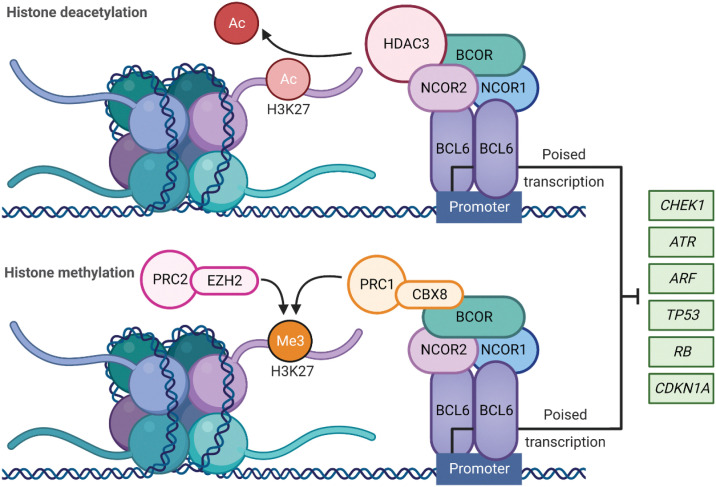
Figure 2.
BCL6 role in transcriptional regulation: BCL6 homodimer binds to target gene promoters to repress the transcriptional programs required for tumor suppression and apoptosis during the formation of the GCs. This is regulated via the recruitment of BCL6 corepressor (BCOR), nuclear receptor corepressor (NCOR1), and nuclear receptor corepressor 2 (NCOR2) to form a multifunctional ternary corepressor complex. BCL6 represses or poises transcription through BCOR and NCOR2 binding to histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3), resulting in deacetylation of H3K27. When BCOR binds and recruits noncanonical polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1)-CBX8, the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) complex subunit enhancer of zester homolog 2 (EZH2) catalyzes H3K27 trimethylation resulting in epigenetic silencing. Ac = acetylation, Me3 = trimethylation. (Created with BioRender.com)