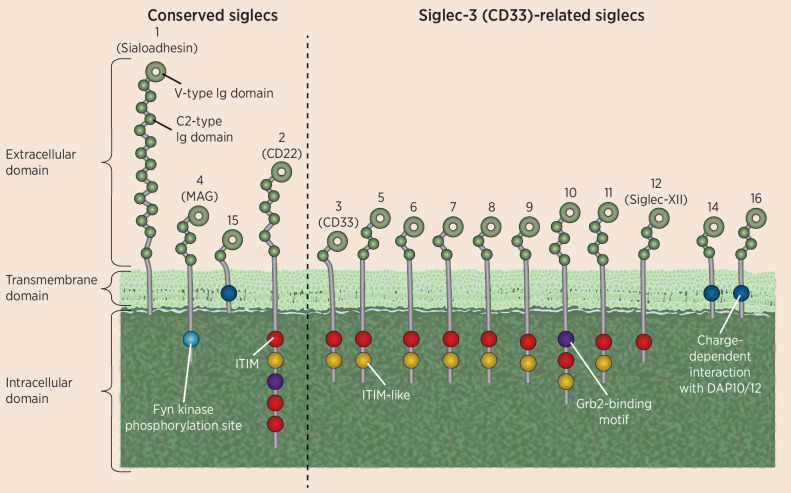
Figure 2.
Illustration of the structure and diversity of Siglecs. There are two main groups of Siglecs, those which are highly conserved, as shown on the left, and a more diverse group of CD33-related Siglecs, as shown on the right. All Siglecs have an extracellular V-type Ig domain and at least one C2-type Ig domain. Many Siglecs also contain at least one cytoplasmic ITIM domain, involved in immunosuppressive signaling.