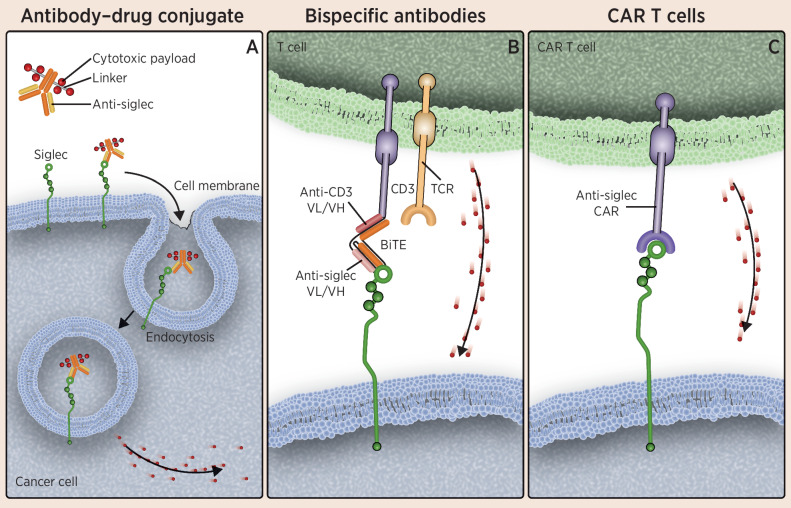
Figure 3.
Therapies targeting Siglecs on malignant myeloid and lymphoid cells. A, Illustrates ADCs composed of an anti-Siglec conjugated to a cytotoxic small-molecule payload. The antibody portion of the drug targets Siglecs, which are displayed on the surface of cancer cells, leading to internalization of the antibody and the drug and subsequent release of the cytotoxic payload within the cancer cell. B, Depicts the use of anti-Siglec BiTEs to link cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, resulting in destruction of the cancer cell. As shown in C, CAR T-cell therapies have been developed that target Siglecs displayed on the surface of cancer cells, leading to cytotoxicity in those cells. Cytotoxic granules are depicted as red dots. TCR, T-cell receptor; VH, variable heavy chain; VL, variable light chain.