Figure 4.
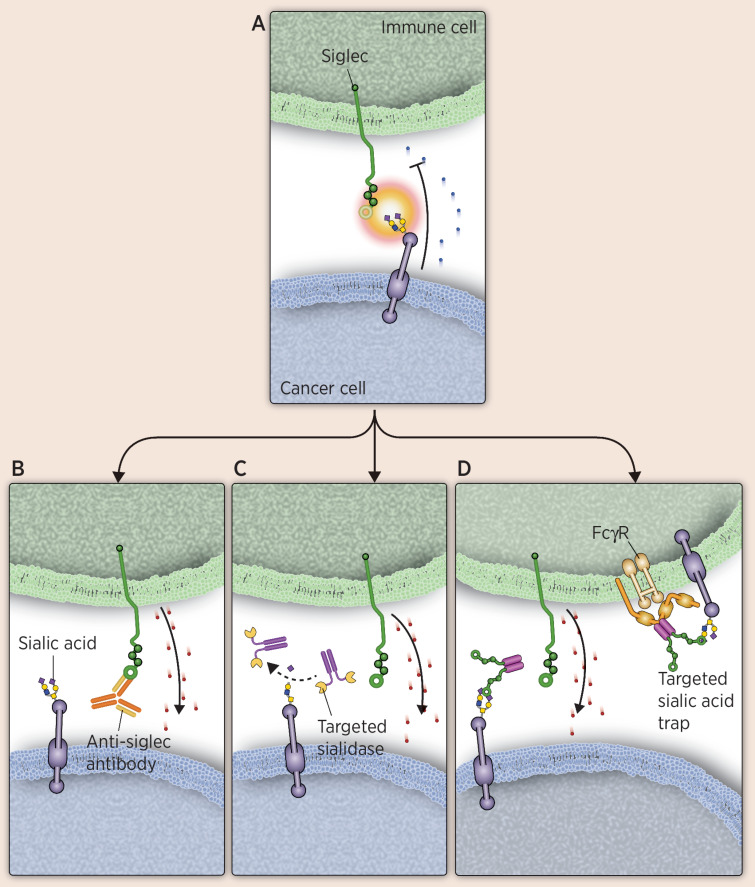
Therapies targeting Siglecs as immune modulators. To overcome immune evasion mechanisms of cancer cells, several approaches are being evaluated, including Siglec-blocking antibodies, targeted sialidases, and targeted sialic acid traps. A, Illustrates an interaction between an inhibitory Siglec on an immune cell and a sialylated glycan on a cancer cell, leading to immunosuppression. B, Illustrates an anti-Siglec binding to a Siglec to block binding, thus preventing their ability to suppress an immune response. C, Shows a sialidase conjugated to an antibody that targets it to cancer cells. Once bound, it desialylates the ligand, preventing immune suppression from Siglec–sialic acid interactions. D, Depicts a Siglec-Fc fusion that functions as a sialic acid trap. The Fc portion allows localization to immune cells, whereas the Siglec portion can bind sialic acid on tumor or immune cells, blocking inhibitory immune signaling. Cytotoxic granules are depicted as red dots.