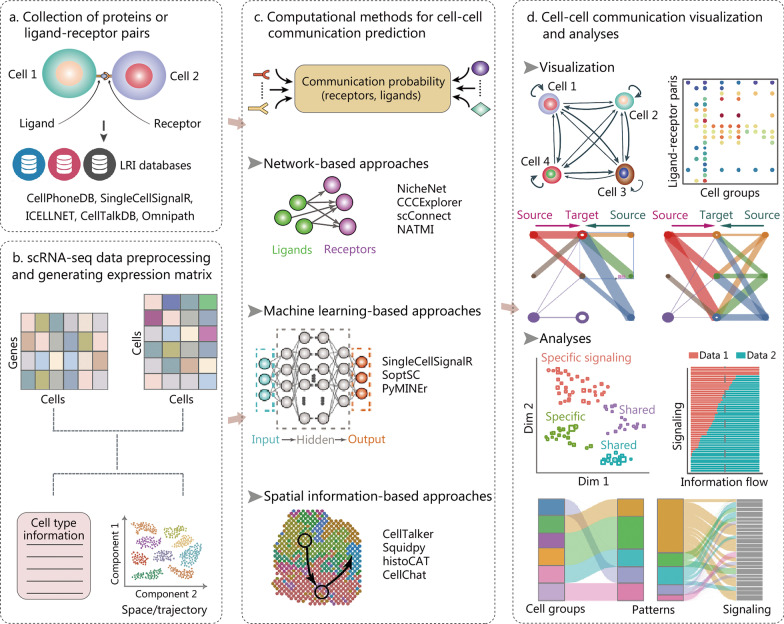
Fig. 3.
The data resources, computational pipelines, and visualization methods used for cell–cell communication (CCC) inference with scRNA-seq data. Typical analysis steps include the collection of ligand-receptor pairs (a), cell clustering and annotation in scRNA-seq (b), computational prediction of CCC (c), followed by results visualization and downstream analysis (d). The CCC inference tools can be categorized into three main classes: network-based, machine learning-based and spatial information-based approaches. LRI ligand-receptor interaction, scRNA-seq single-cell RNA sequencing, CCCExplorer cell–cell communication explorer, NATMI network analysis toolkit for multicellular interactions, histoCAT histology topography cytometry analysis toolbox, SoptSC similarity matrix-based optimization for single-cell data analysis, PyMINEr Python maximal information network exploration resource, Squidpy spatial quantification of molecular data in Python