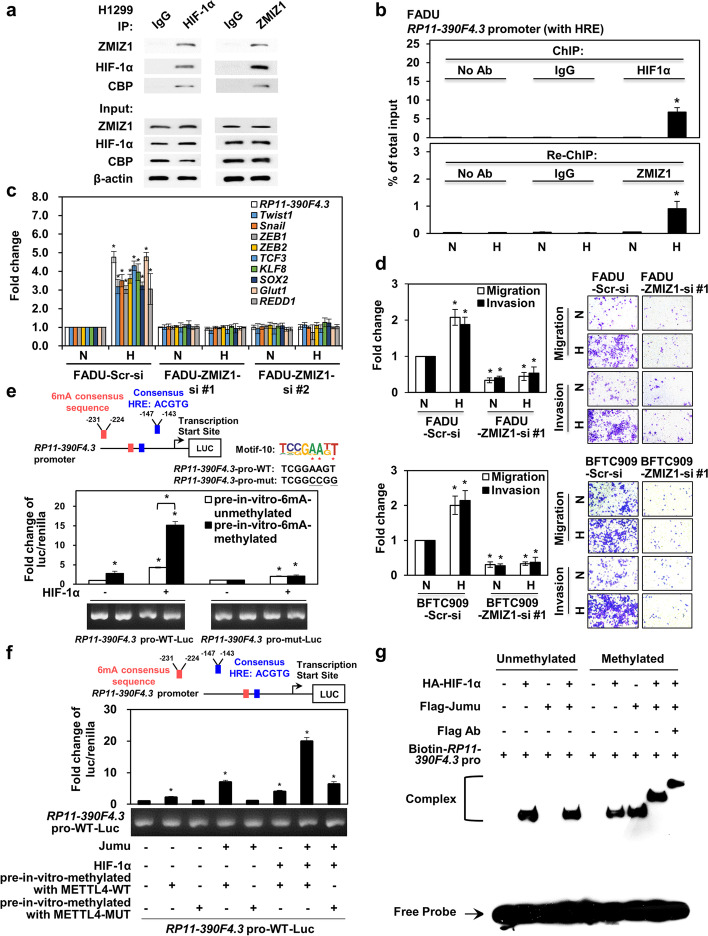
Fig. 6.
Characterizations of ZMIZ1 and synergistic activation by HIF-1α and Jumu using different in vitro assays. a Co-IP assays show the interaction between HIF-1α, ZMIZ1, and CBP. IgG was used as a control. b ChIP-re-ChIP assays show that ZMIZ1 could be pulled down after HIF-1α IP. N, normoxia; H, hypoxia. No antibody/normoxia condition was used as a control. c Knockdown of ZMIZ1 decreased the induction of various HIF-1α target genes. Knockdown using the scrambled control siRNA was used as a control. N, normoxia; H, hypoxia. d Knockdown of ZMIZ1 decreased the in vitro migration and invasion activity induced by hypoxia in FADU and BFTC909 cell lines. N, normoxia; H, hypoxia. Normoxic condition was used as a control. e Reporter gene assays show that the 6mA site pre-methylated RP11-390F4.3 promoter-driven reporter construct has higher luciferase activities compared to the unmethylated reporter construct after co-transfection with a HIF-1α expression vector. The positions of the 6mA consensus sequence and the HIF-1α response element are shown in the upper part of the panel. The luciferase/renilla activities of FADU cells co-transfected with reporter construct and pcDNA3 control vector were used as the baseline control. The amounts of plasmids transfected inside cells are shown in agarose gels. f Reporter gene assays show that HIF-1α and Jumu (a Drosophila 6mA-binding protein) synergistically activated the lncRNA RP11-390F4.3 promoter-driven reporter construct in which its 6mA site on the promoter was pre-methylated. The upper part of the panel shows the positions of the 6mA consensus sequence and the consensus HRE on the RP11-390F4.3 promoter. The controls were the same as in e. g DNA EMSA assays show the cooperative binding between HIF-1α and Jumu when the oligonucleotides containing the 6mA consensus sequence were in vitro methylated. The positions of the free probe and of the protein complexes are indicated on the left. The asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance (P<0.05) between experimental and control groups