Figure 2.
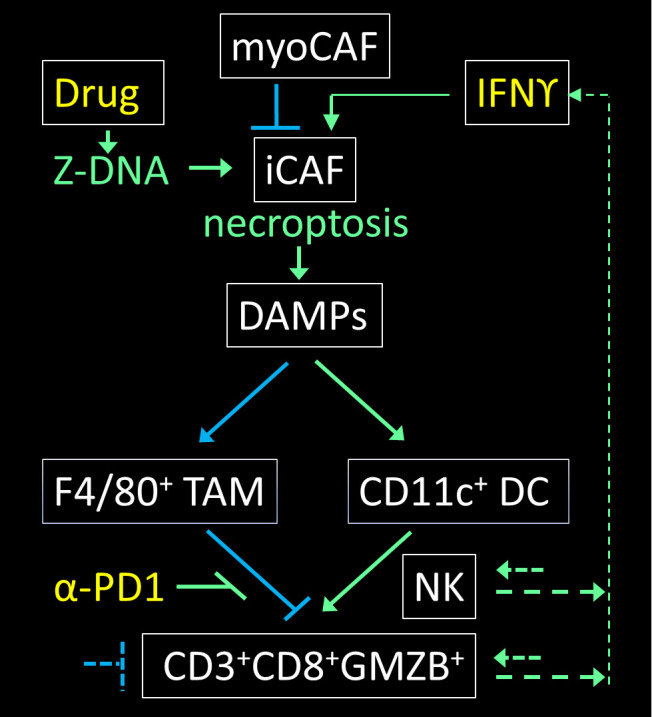
ZNA induced by a small molecule bypasses the need for ADAR1 inhibition and directly activates ZBP1 to induce necroptosis in iCAFs. The DAMPs released induce both immunosuppressive TAMs (tumor associated macrophages) that express the F4/80 adhesion protein and immunostimulatory CD11c+ DCs (dendritic cells). The amplification of anti-cancer cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells is favored by ICB with antibodies like anti-PD1 (α-PD1) that prevent binding of the PDL1 and PDL2 ligands expressed by TAMs to the immune-inhibitory programmed cell death 1 (PD1) receptor expressed on T cells. The net effect of α-PD1 is stimulatory as it negates a negative interaction. The antitumor immune cells, along with bystander cells, also produce cytokines that signal through the JAK1/STAT1 pathway and, by enhancing ZBP1 expression in iCAFs, increase the vulnerability of these cells to necroptosis.11 15 46 Stimulatory effects are indicated with green arrows while inhibitory pathways are colored blue with therapeutic agents amplifying antitumor responses labeled yellow. The arrows with a blunt end indicate suppressive interactions, while the dotted lines are representative of additional nodes that are potentially targetable but that are not detailed here. DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; F4/80, adhesion G protein-coupled receptor E1 encoded by ADGRE1; iCAF; inflammatory CAF; ICB, immune checkpoint blocker; IFN, interferon; JAK/STAT, Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription; PDL1, programmed cell death ligand 1; myoCAF (α-smooth muscle actin (encoded by ACTA2) positive cancer-associated myofibroblasts);TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; ZBP1, ZNA binding protein 1; ZNA, Z-DNA or Z-RNA collectively.
