Figure 3.
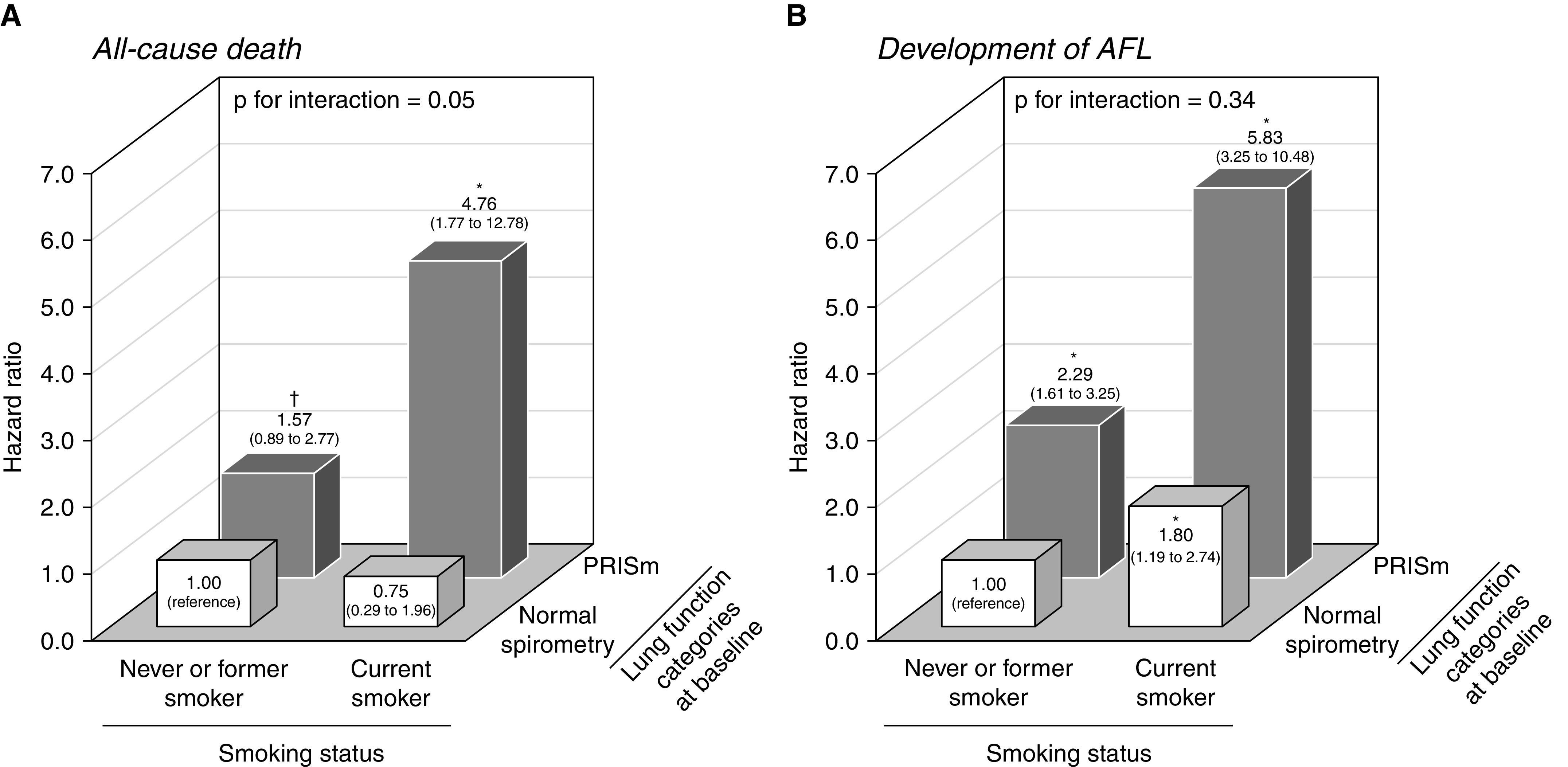
The combined influence of PRISm at baseline and current smoking on (A) the risk of all-cause death and (B) the development of airflow limitation. The hazard ratio of all-cause death (A) was estimated in 2,509 participants without airflow limitation at baseline and adjusted for age, sex, smoking pack-years, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, electrocardiogram abnormalities, history of cardiovascular disease, history of cancer, alcohol intake, and regular exercise. The hazard ratio of the development of airflow limitation (B) was estimated in 2,250 participants with normal spirometry or PRISm at baseline and adjusted for age, sex, smoking pack-years, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, current drinking, regular exercise, and FEV1 as a percentage of FVC at baseline. *P < 0.05 and †P < 0.20 versus the reference group (never or former smokers and participants with normal spirometry at baseline). AFL = airflow limitation; PRISm = preserved ratio impaired spirometry.
