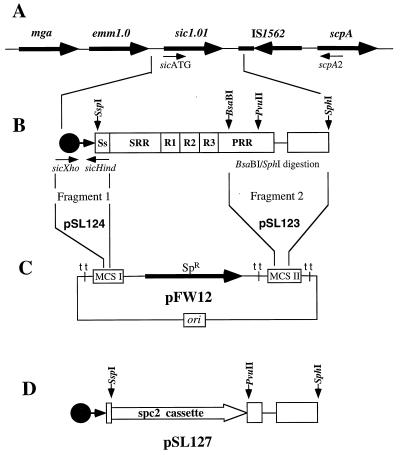
FIG. 3.
Construction of the suicide plasmid pSL127, used to generate an sic1.01-inactivated MGAS 5005. All primers and restriction sites used in the cloning strategy are shown. (A) Schematic representation of the Mga regulon with the sic gene in MGAS 5005 (not to scale). The map was drawn based on PCR analyses using different combinations of primers specific for the emm1.0, sic1.01, IS1562, and scpA genes. (B) DNA region containing the sic gene and part of the IS1562 used in plasmid construction. Major parts of the sic sequence are shown: Ss, signal sequence; SRR, short repeat region; R1 to R3, repeat regions 1 to 3; PRR, proline-rich region. Two chromosomal fragments from MGAS 5005 were amplified. Fragment 1 (∼150 bp), flanked by the PCR-generated XhoI (sicXho [TCGACTCGAGGTTAAGGAGAGGTCAC]) and HindIII (sicHind [TTTTCAAGCTTATTTCTAATATTC]) sites, contained the sic promoter region and first 26 bp of the coding region. Fragment 2 (∼830 bp), obtained by restriction digestion of the PCR product (sicATG [GGAGAGAATACTAATGAATATTAG] and scpA2 [CTGGTGTATCAGCAGTTTTAGC]) with restriction enzymes BsaBI and SphI, contained a 3′ end of the sic proline-rich region and adjusted part of IS1562. (C) First, fragment 2 was cloned into multiple cloning site (MCS) II of the E. coli vector pFW12, generating plasmid pSL123. Next, fragment 1 was cloned into MCS I of the pSL123, resulting in construct pSL124. (D) In the last step, the nonpolar spc2 cassette was cloned in frame between the SspI and PvuII sites of the sic coding sequence, replacing the original spectinomycin resistance marker (SpR) of the vector. In this plasmid, designated pSL127, the spc2 insertion limits the amount of the sic coding region to 6 bp (2 amino acids) at the 5′ end and 129 bp (43 residues) at the 3′ end. Suicide plasmid pSL127 was used to generate an sic-inactivated isogenic variant of MGAS 5005.