Fig. 9.
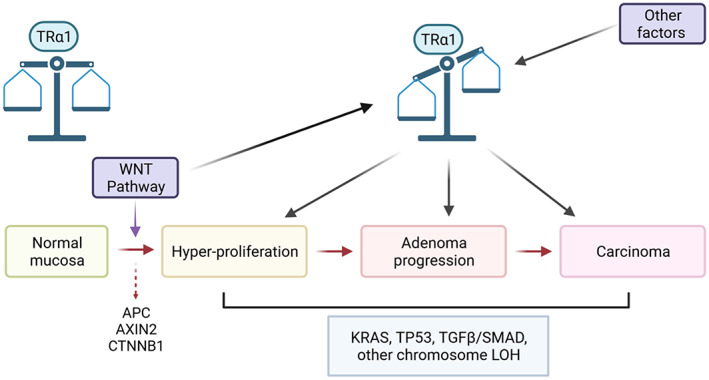
Interplay between TRα1 and the Wnt pathway and correlation with gene deregulation during intestinal tumorigenesis. The picture summarizes the known sequential genetic alterations that are frequently associated with colorectal tumorigenesis in humans. APC/AXIN2/CTNNB1 gene mutations, which are responsible for Wnt/β‐catenin overactivation, are key events that occur during the early stage of cell transformation. The other indicated mutations are more frequently associated with later stages [88]. Interestingly, together with the control of the Wnt pathway by TRα1 and its association with the various steps in CRC (hyperproliferation, adenoma progression, and carcinoma generation) [14, 15], our new data point to regulation of the THRA promoter by the Wnt pathway and regulation of TRα1 expression by increased Wnt activity in very early stages of tumor development. LOH, loss of heterozygosity. The figure was created with BioRender.com (agreement number: TX23QDYSJV).
