Figure 6. ACT of oncolytic virus-induced TILs led to significant therapeutic efficacy in mice bearing peritoneal carcinomatosis of MC38 colon cancer.
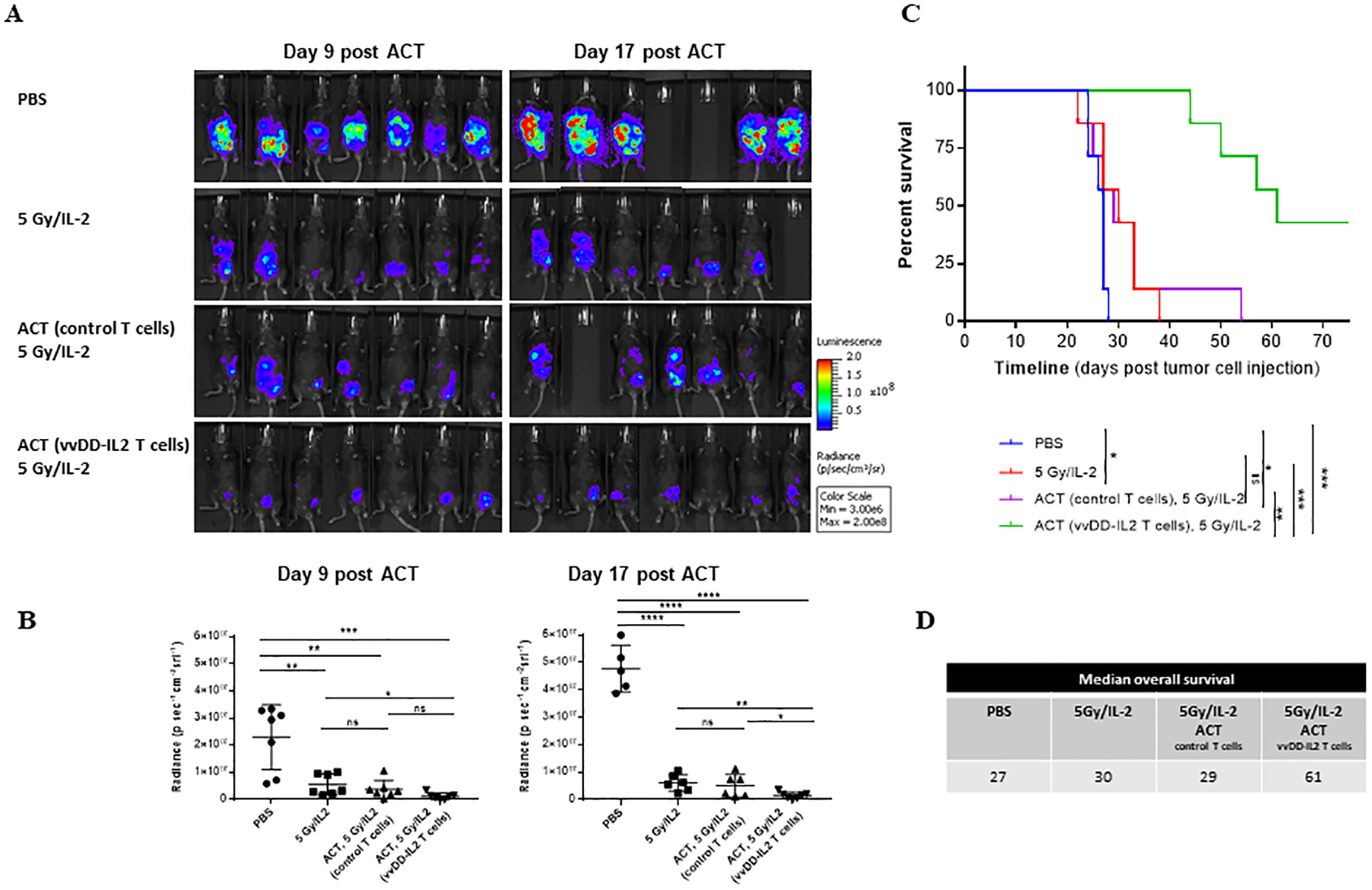
B6 mice were intraperitoneally inoculated with 5 × 105 MC38-luc cancer cells followed in 7 days, these mice were imaged for tumor growth and randomly grouped (n = 7 mice/group). Prior to ACT, mice in the treated groups received 5 Gy of sublethal irradiation. Grouped mice were intraperitoneally injected with PBS, naïve T cells, or vvDD-IL2 induced and ex vivo expanded TILs. All treated mice received exogenous IL-2 (1.0e5 IU/mouse, i.p. injection once every ~12 h for 3 days). One experiment representative of two independent experiments is shown (A, B). (A). Tumor growth has been monitored by live animal imaging 9 days and 17 days post treatment. (B). Radiance data quantified for two time points at days 9 and 17 post ACT. Student’s t-test was used to analyze the statistical significance. The variance was similar between the groups in this experiment. (C). The long-term survival of tumor-bearing mice was monitored by Kaplan-Meier analysis. These data represent one of the two independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (D). Summary of median survival in the different treatment groups. This experiment was performed 2 times.
