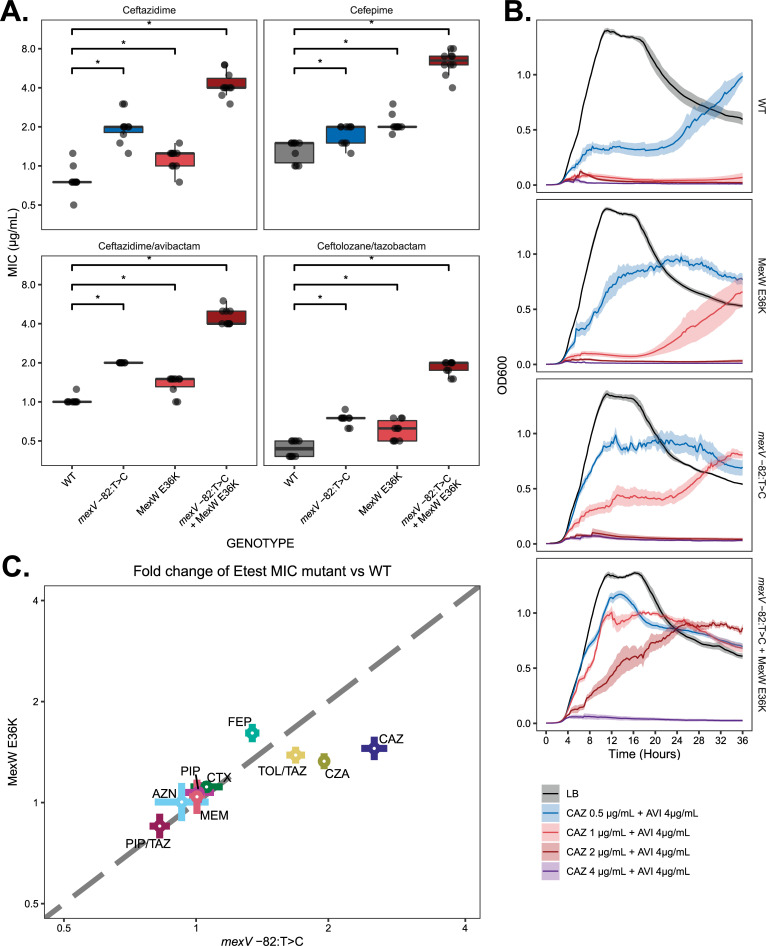
Fig 4. MexVW efflux pump mutations introduced into a WT MPAO1 strain confer resistance to cephalosporins and cephalosporin/beta-lactamase combination antibiotics.
(A) Gradient diffusion (E-test) MICs for MPAO1-WT, mexV -82:T>C, MexW E36K, and double mutant (n = 10 per antibiotic/genotype combination). The boxes display the median with the lower and upper hinges corresponding to the first and third quartiles. Brackets with asterisks above the plot indicate statistical significance with respect to MPAO1-WT (Wilcoxon 2-sided p-value < 0.05). All pairwise comparisons between mutants were statistically significant as well (S7 Table). (B) Growth curves of MexVW engineered strains at 37°C in LB broth with a range of ceftazidime concentrations with fixed 4 μg/mL avibactam concentration. Lines represent the median OD600 of 7 biological replicates per time point, with shaded envelope representing the standard error of the mean. (C) Scatterplot showing the relative contribution of the mexV -82:T>C and MexW E36K mutations to resistance to each antibiotic. Each colored point represents the mean ratio of gradient diffusion MIC in the corresponding mutant strain to that in the parental MPAO1 strain, with error bars represent the corresponding standard error of the mean. A dashed line of equality is included. The underlying data to generate this figure can be found in S2 Data. AZN, aztreonam; CAZ, ceftazidime; CTX, cefotaxime; CZA, ceftazidime/avibactam; FEP, cefepime; MEM, meropenem; PIP, piperacillin; PIP/TAZ, piperacillin/tazobactam; C/T, ceftolozane/tazobactam; WT, wild type.