Figure 9.
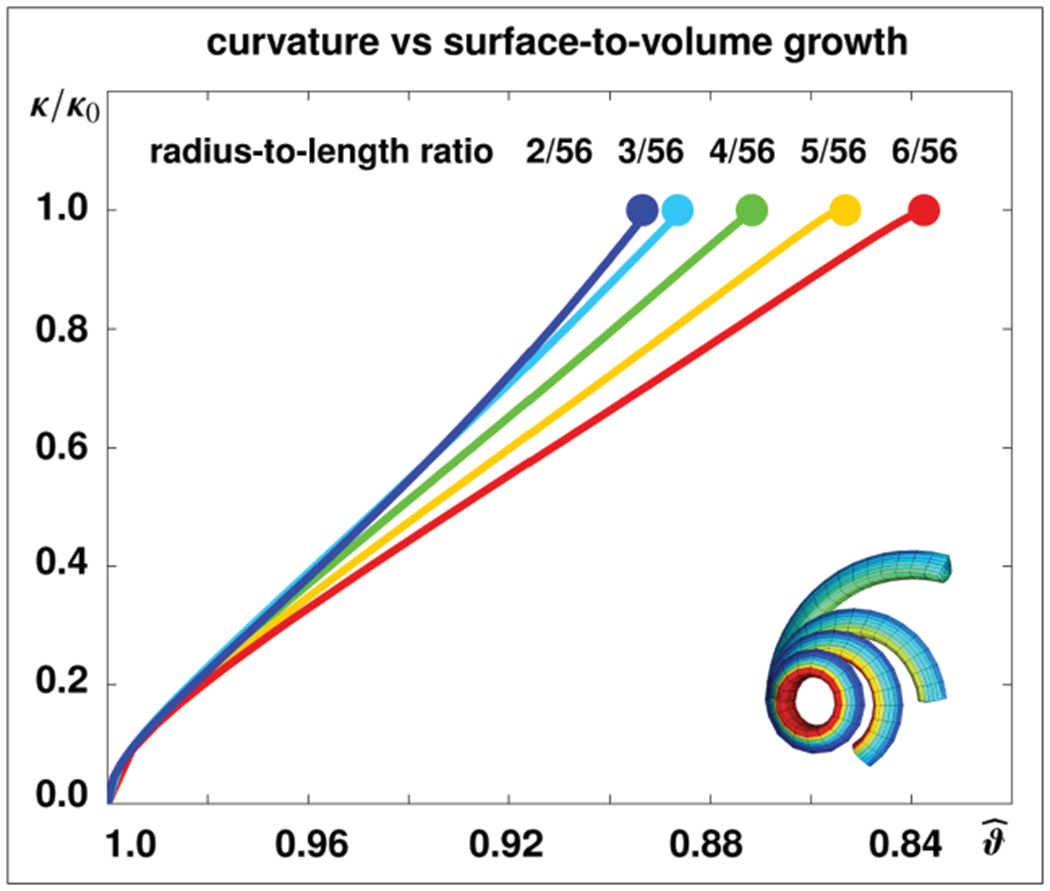
Growth-induced curvature changes in stalk of rhubarb for different radius-to-length ratios. A decrease in the surface-to-volume growth ratio increases tissue tension and induces an increase in relative curvature κ/κ0. At a relative curvature of κ/κ0 = 1.0, indicated throughout the solid dots, each stalk forms a closed loop. The surface-to-volume growth ratio required to form a closed loop, as shown in Figure 10, bottom row, decreases with increasing radius-to-length ratios, from , to , , , and , from blue to red.
