TABLE 4.
Relationships between ferritin BAZs as mediated by inflammation among PSC (6–59 months) with normal weight to overweight or obesity by survey in the BRINDA project1
| CIC2 | Country, survey year | n | PSC mediation analyses, adjusted3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total effect | Direct effect | Indirect effect | Mediated, % | Mediated by CRP, % | Mediated by AGP, % | |||
| Low | Afghanistan, 2013 | 595 | −2.8 (−11.7, 6.0) | −1.9 (−10.8, 7.0) | −0.9 (−2.8, 1.1) | NM | — | — |
| Bangladesh, 2010 | 1179 | −6.5 (−11.0, −2.3) | −5.7 (−10.1, −1.6) | −0.8 (−2.2, 0.5) | NM | — | — | |
| Bangladesh, 2012 | 368 | −4.8 (−15.3, 5.5) | −2.7 (−12.6, 7.1) | −2.2 (−6.1, 1.7) | NM | — | — | |
| Burkina Faso, 2010 | 63 | −10.5 (−41.9, 19.8) | −10.6 (−37.8, 15.4) | 0.1 (−7.5, 7.7) | NM | — | — | |
| Cambodia, 2014 | 599 | −6.2 (−16.6, 3.8) | −7.0 (−16.6, 2.0) | 0.9 (−3.3, 5.0) | NM | — | — | |
| Côte d'Ivoire, 2007 | 435 | 1.4 (−7.2, 10.0) | −0.6 (−8.6, 7.4) | 2.0 (−2.2, 6.2) | NM | — | — | |
| Kenya, 2007 | 665 | −7.3 (−−16.8, 1.6) | −7.2 (−16.0, 1.1) | −0.1 (−2.7, 2.5) | NM | — | — | |
| Kenya, 2010 | 551 | −5.0 (−13.4, 3.2) | −7.3 (−15.0, −0.2) | 2.5 (−1.8, 6.7) | NM | — | — | |
| Laos, 2006 | 443 | −5.8 (−18.2, 6.2) | −4.5 (−17.2, 7.9) | −1.3 (−5.0, 2.3) | NM | — | — | |
| Liberia, 2011 | 956 | −1.6 (−6.9, 3.7) | −1.7 (−7.2, 3.8) | 0.1 (−1.9, 2.1) | NM | — | — | |
| Malawi, 2016 | 748 | −3.0 (−16.4, 10.4) | −1.5 (−8.5, 5.4) | 1.3 (−1.5, 4.0) | NM | — | — | |
| Mongolia, 2006 | 239 | −0.2 (−7.2, 6.7) | −1.9 (−15.0, 11.2) | −1.1 (−3.9, 1.7) | NM | — | — | |
| Nicaragua, 2005 | 946 | −9.0 (−17.2, −1.7) | −9.5 (−16.8, −3.1) | 0.5 (−1.4, 2.4) | NM | — | — | |
| Zambia, 2009 | 330 | −8.6 (−20.1, 2.0) | −9.2 (−20.0, 0.8) | 0.6 (−4.1, 5.4) | NM | — | — | |
| Low-middle | Cameroon, 2009 | 556 | 12.9 (4.6, 19.7) | 12.5 (4.9, 18.7) | 0.3 (−1.8, 2.5) | NM | — | — |
| Georgia, 2009 | 2064 | 0.3 (−2.5, 3.1) | 0.3 (−2.5, 3.1) | −0.02 (−0.1, 0.1) | NM | — | — | |
| Nigeria, 2012 | 303 | −2.6 (−10.8, 5.5) | −3.8 (−13.2, 5.5) | 1.2 (−2.2, 4.7) | NM | — | — | |
| Pakistan, 2011 | 5824 | −3.0 (−5.6, −0.5) | −3.1 (−5.8, −0.6) | 0.1 (−0.1, 0.3) | NM | — | — | |
| Philippines, 2011 | 1656 | −6.2 (−12.6, −0.1) | −4.3 (−10.7, 1.9) | −2.0 (−3.7, −0.2) | 31% | 8% | 23% | |
| Vietnam, 2010 | 344 | −11.8 (−19.4, −5.8) | −11.1 (−19.1, −4.3) | −0.9 (−2.5, 0.7) | NM | — | — | |
| Upper-middle | Azerbaijan, 2013 | 987 | −2.1 (−6.9, 2.7) | −0.1(−4.6, 4.3) | −2.0 (−4.2, 0.2) | NM | — | — |
| Colombia, 2010 | 7753 | −4.8 (−7.9, −1.9) | −4.7 (−7.8, −1.8) | −0.2 (−0.6, 0.3) | NM | — | — | |
| Mexico, 2006 | 1562 | −3.2 (−9.0, 2.5) | −3.4 (−9.3, 2.4) | 0.2 (−1.3, 1.8) | NM | — | — | |
| Mexico, 2012 | 2454 | −5.8 (−9.6, −2.3) | −6.5 (−10.3, −3.2) | 0.8 (−0.3, 1.8) | NM | — | — | |
| High | United States, 2006 | 1081 | −5.8 (−9.6, −2.3) | −6.5 (−10.3, −3.2) | 0.8 (−0.3, 1.8) | NM | — | — |
Ferritin, CRP, and AGP variables were natural-log transformed for analysis due to nonnormal distributions. Mediation estimates were exponentiated, and results are presented as percentage changes (95% CIs) in ferritin for every 1-unit change in BAZ. Ferritin concentrations were measured in serum or plasma, as reported in the survey. All estimates account for a cluster survey design (cluster, strata) with survey weights applied, except in the survey from Mongolia, which used simple random sampling. The inclusion criteria were having a BAZ or WHZ ≥ −2 SD and a negative malaria test result. AGP, alpha-1-acid glycoprotein; BAZ, BMI-for-age z-score; BRINDA, Biomarkers Reflecting Inflammation and Nutritional Determinants of Anemia; CIC, country income classification; CRP, C-reactive protein; NM, no mediation; PSC, pre-school age children; WHZ, weight-for-height z-score.
CIC was defined according to the World Bank definition for the year in which the survey was conducted (38).
Model for mediation analyses:
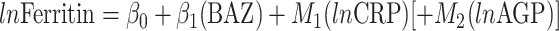 (2)
(2)
Here, all values were continuous and AGP was included as a mediator only in analyses for which it was available in the data set. Interpretation was as follows: total effect is the effect of BAZ on ferritin; direct effect is the effect of BAZ on ferritin, controlling for inflammation; and indirect effect is the effect of BAZ on ferritin as mediated by the effect of CRP or AGP. Mediation was considered present when both the total and indirect effects were significant (41). The covariates available for adjustment were age, education level (respondent or maternal education level), household socioeconomic status, access to an improved water source, access to an improved toilet, and urban or rural residence. Covariates were included in the mediation model if they were associated with the outcome variable at a P value < 0.1 in bivariate models (Supplemental Table 6). Unadjusted mediation estimates are presented in Supplemental Table 11.
