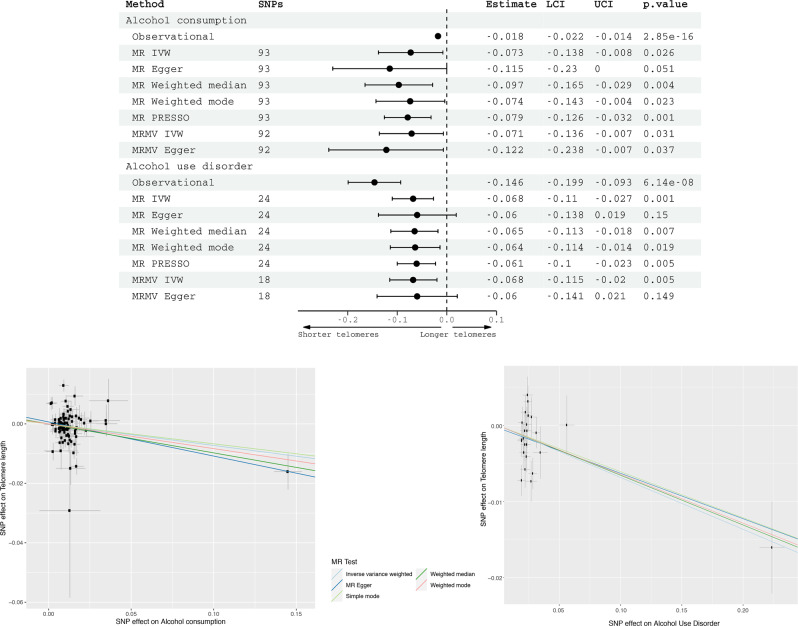
Fig. 2. Top - Multivariable-adjusted observational estimates (in 245,354 UKB participants) and two-sample Mendelian randomization estimates (two-sample design) for the association of genetically predicted alcohol consumption and alcohol use disorder with telomere length.
Estimates for alcohol consumption observational associations represent SD change in telomere length for 1 SD increase in alcohol units weekly. MR estimates for alcohol consumption are per SD increase in genetically predicted log-transformed alcoholic drinks per week, and for AUD having a diagnosis of AUD. Bottom—SNP effects are plotted. A non-zero gradient to the lines indicates evidence for causality of alcohol on telomere length. Abbreviations: MR Mendelian randomization, SNPs single nucleotide polymorphisms, IVW inverse variance weighted, PRESSO Mendelian Randomization Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier, MRMV multivariable Mendelian randomization.