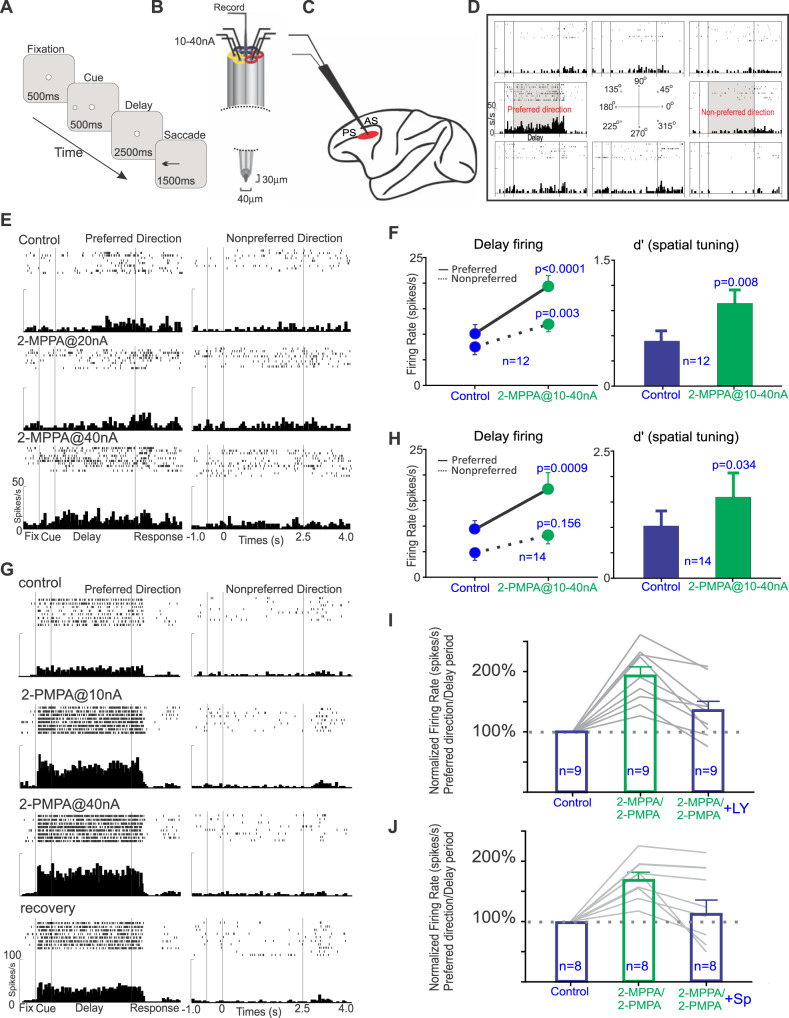
Fig. 4. The effects of iontophoretic application of GCPII inhibitors onto dlPFC Delay cells in aged monkeys performing an oculomotor delayed response task.
A The oculomotor delayed response task. B The iontophoretic recording electrode. C The recording site in dlPFC; PS = principal sulcus; AS = arcuate sulcus. D An example of a dlPFC Delay cell, with spatially-tuned persistent firing for its preferred direction (180°). E An example of the effects of iontophoresis of 2-MPPA onto a dlPFC Delay cell in an aged female monkey with weak task-related firing under control conditions. F the average effects of 2-MPPA on dlPFC delay-related firing in Delay cells from both monkeys. G An example of a dlPFC Delay cell whose firing for its preferred direction is greatly increased by 2-PMPA in a middle-aged male monkey. H population response for 2-PMPA. I The enhancing effects of 2-MPPA or 2-PMPA were significantly reversed by co-application of the mGluR2/3 antagonist, LY341495. J The enhancing effects of 2-MPPA or 2-PMPA were significantly reversed by co-application of the PKA activator, Sp-cAMPS. Note that Sp-cAMPS activates PKA signaling, but is downstream from cAMP-HCN channel signaling, and thus may have only partial actions in reversing the beneficial effects of NAAG-mGluR3 signaling.