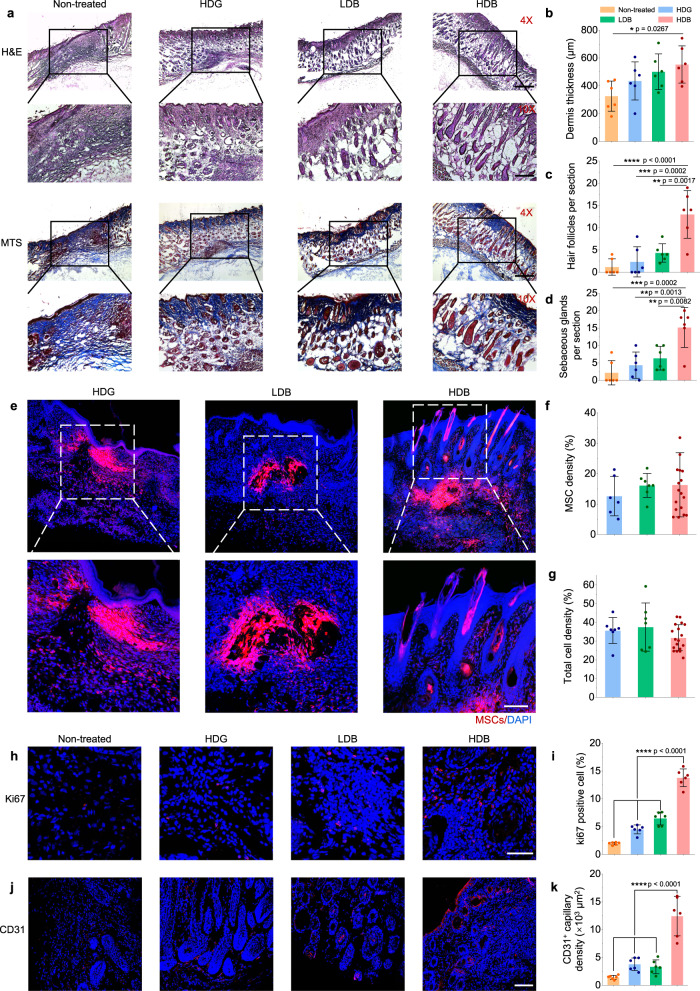
Fig. 8. Matrigel HDB-MSCs augment skin wound healing and hair follicle regeneration.
a Representative images of H&E staining and MTS of regenerated skin tissues at 3 weeks post-printing (or post-casting) of MSCs loaded in Matrigel HDG, LDB beads, and HDB beads, respectively. For the HDB group, the MSCs-laden HDB beads were printed in sparse patterns, and the empty space was filled with acellular Matrigel beads. Scale bars: 500 µm (4×, upper row), 200 µm (10×, lower row). b–d Quantification of dermis thickness (b) and hair follicle (c) and sebaceous glands (d) counts per section in the regenerated area. n = 6. Six sections are selected. e–g Representative images of MSCs in the Matrigel HDG, LDB, and HDB groups after transplantation for 1 week (e) and quantification of MSCs intensity (f) and total cell density (g) per section in skin tissues. MSCs were labeled using the red Dil cell membrane tracker (Meilunbio). n = 3. Scale bar, 100 µm. h, i Immunostaining for Ki67 to view the proliferating cells (h) and quantification of Ki67 positive cells per section (i). Scale bar, 50 µm. n = 6. j, k, Immunofluorescence for CD31 to view angiogenesis (j) and quantification of CD31 positive capillaries (k). Scale bar, 100 µm. n = 6. For each data, at least six imaging windows are randomly selected. All data are expressed as mean ± SD. Significant difference is determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.