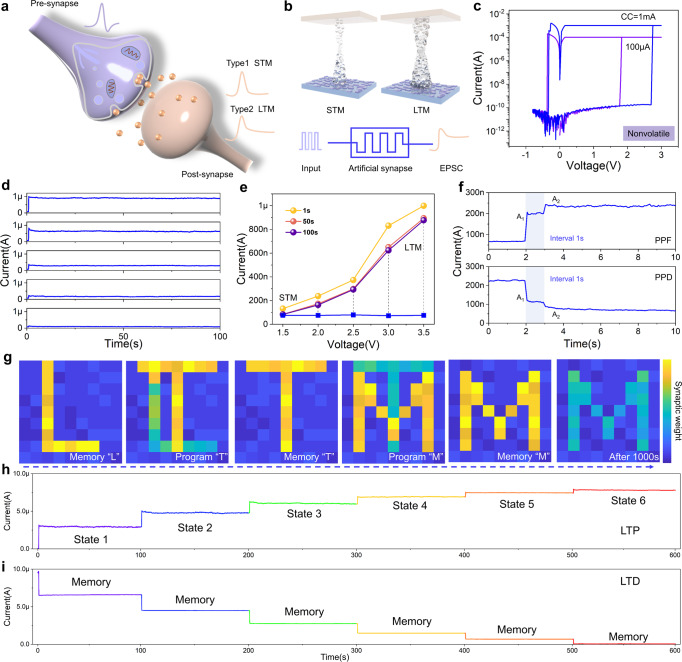
Fig. 2. Nonvolatile storage characteristic of artificial synapse.
a Schematic of biological synapse, which could be emulated by artificial synapses with short-term and long-term plasticity. b Schematic of switching mechanism for short-term memory (STM) and long-term memory (LTM) in artificial synapse. Excitatory post-synaptic current (EPSC) could be inspired by electrical pulse applied to device. c Nonvolatile resistive switching curves with compliance current (CC) of 100 μA and 1 mA. d EPSC behaviors of artificial synapse under different electrical pulse amplitudes, including 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, and 3.5 V. e Device transition from STM to LTM as a result of enhanced pulse amplitude, extracted from panel d. f Paired pulse facilitation (PPF) and paired pulse depression (PPD) characteristics generated by a pair of pulses with an interval of 1 s. g Real-time program and storage for letters of “L”, “T” and “M” based on synaptic weights of memristor array. h, i Long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) curves of artificial synapses with multi-level storage states, respectively.