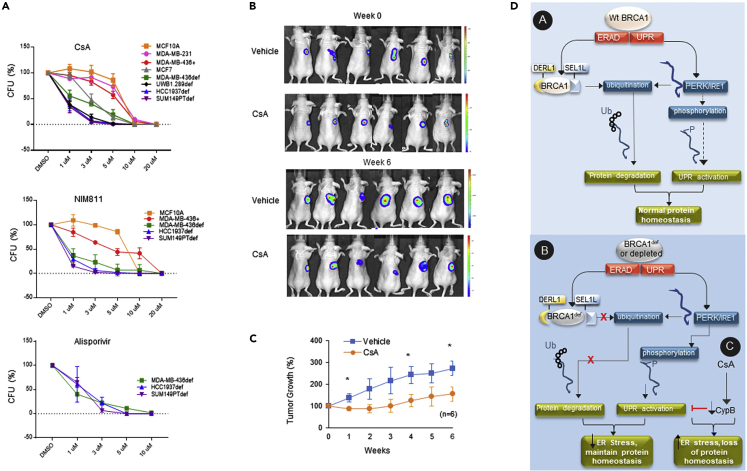
Figure 5.
Cyclophilin inhibitors induce severe synthetic lethality in BRCA1-def cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
(A) BRCA1-def cancer cells (MDA-MB-436, HCC1937, SUM149PT or UWB1.289), BRCA1-proficient cancer cells (MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-231 or MCF7) and non-tumorigenic mammary epithelial cells (MCF10A) were seeded one day prior to drug treatment. A single continuous dose of CsA, NIM811 or Alisporivir was added to the corresponding cell lines. Quantitative analysis of each survival curve is shown in graphs. CsA = Cyclosporin A. CFU = Colony forming units. DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle.
(B) CsA treatment of human BRCA1-def breast cancer cells in a murine model. Representative luciferase images of each treated subject were taken by an In Vivo Imaging systems (IVIS). Animals were either treated with vehicle (control) or CsA (treatment) for 6 weeks post-tumor formation.
(C) Quantitative analysis of tumor progression from each group was summarized in graph.
(D) Schematic diagram depicts the model of wildtype and mutant BRCA1 regulation of the ERAD and UPR signaling pathways to maintain protein homeostasis in the ER. Wt = wildtype. def = deficient. Ub = ubiquitin. P = phosphate. Dashed arrow = less favored pathway. Ubiquitination and phosphorylation modifications in the diagram are simplified for clarity. Data are displayed as mean ± SD. P values were calculated by Student’s two-tailed, unpaired t-test.