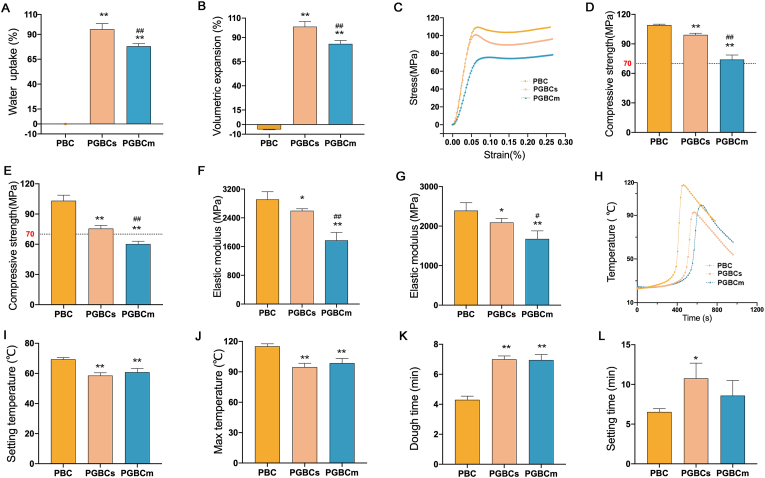
Fig. 2.
Characterization of the properties of the bone-filling materials. Water uptake (A) and volumetric expansion (B) of PBC, PGBCs, and PGBCm(n = 5). Representative stress-strain curves (C), compressive strengths (D, E), and elastic moduli (F, G) of the materials before (D, F) and after (E, G) water immersion (n = 5). Representative time-temperature curves (H), setting temperatures (I, n = 3), max temperatures (J, n = 3), dough times (K, n = 5), and setting times (L, n = 3) of each bone cement. (∗ indicates a significant difference between PGBCs or PGBCm and PBC, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.005; # indicates a significant difference between PGBCs and PGBCm, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.005).