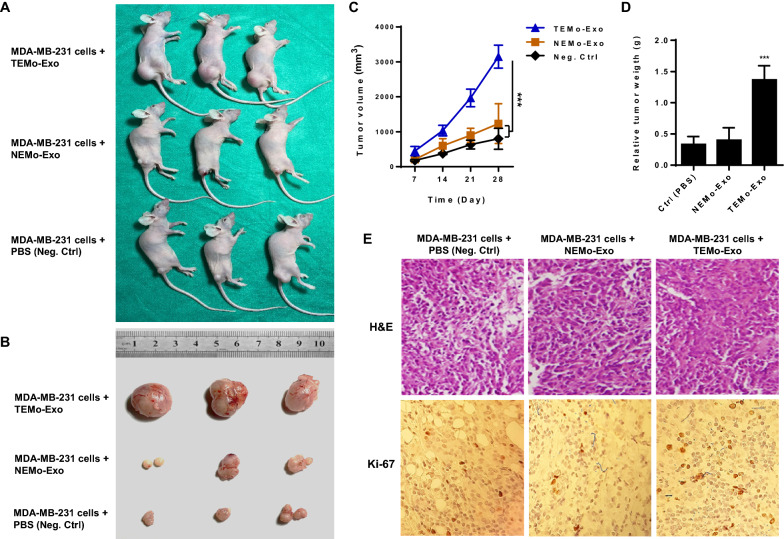
Fig. 6.
Exosomes derived from TEMo promote breast tumor growth in vivo. A Representative images of tumor-bearing nude mice subcutaneously implanted with MDA-MB-231 cells alone or mixed with exosomes derived from TEMo or NEMo. B Representative photographs of xenograft tumors obtained from mice at day 28 post-implantation. C Tumor volume at days 7, 14, 21, and 28 after subcutaneous implantation of nude mice with MDA-MB-231 cells alone or mixed with 200 µg/mL exosomes derived from TEMo or NEMo. Co-implantation of MDA-MB-231 BC cells and TEMo-Exo together resulted in a faster growth rate of tumors and a larger tumor diameter than that of mice injected with either BC cells alone or BC cells mixed with NEMo Exo. ***P-value < 0.001. D Tumor weight in mice implanted with MDA-MB-231 BC cells mixed with 200 µg/mL TEMo-Exo was significantly higher than in those implanted with BC cells alone or mixed with NEMo Exo at day 28 post-implantation. ***P-value < 0.001. E Representative photographs of H&E and IHC staining for Ki-67 on formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded MDA-MB-231-derived xenograft tumor sections from different treatment groups. IHC analysis of the cell proliferation marker Ki67 showed much higher immunoreactivity for nuclear Ki67 in the TEMo-Exo co-implantation group compared to the cell-only group or cells implanted with NEMo-Exo. **P-value < 0.01, ***P-value < 0.001