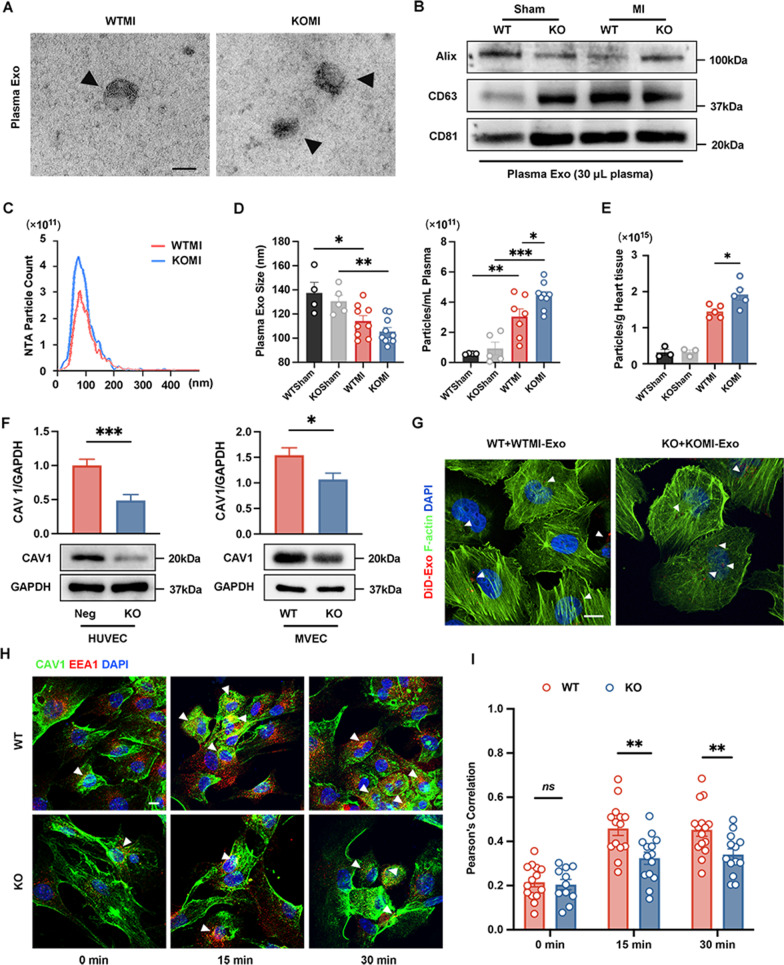
Fig. 3.
CD44 depletion impacts exosome biogenesis and weakens the CAV1-dependent exosome uptake. (A-D) The characteristics of mouse plasma exosomes 1 week after MI. A Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) identified WTMI and KOMI plasma exosomes. Black arrows showed exosomes. Scale bar: 100 nm. B Plasma exosomes extracted from the WTSham, KOSham, WTMI, and KOMI groups were examined with Western blot analysis of exosome markers (Alix, CD63, and CD81). n = 3. C Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) identified plasma exosomes of the WTMI and KOMI groups. D The concentration of plasma exosomes in the WTSham (n = 4), KOSham (n = 5), WTMI (n = 9), and KOMI (n = 10) groups (left panel). The statistical data of plasma exosome sizes in the four groups (right panel). E Quantification of cardiac exosomes isolated from CD44 WT and KO injured LV measured using NTA. F Western blot analysis examined the expression of caveolin1 (CAV1) in CRISPR/Cas9-CD44 KO HUVECs and primary mouse CD44 KO MVECs. n=3. G Representative confocal microscopy images of the uptake of DiD-labeled WTMI-Exo and KOMI-Exo (red) by WT and KO MVECs. Phalloidin marks the cytoskeleton (F-actin, green). n = 6. DAPI (blue) stained cell nuclei. Scale bar: 10 μm. H Representative confocal microscopy images of plasma exosomes internalized by primary mouse MVECs within 0 min, 15 min, and 30 min. White arrowheads showed the colocalization of CAV1 (green) and the early endosome marker early endosome antigen 1 (EEA1) (red) in MVECs. DAPI (blue) stained cell nuclei. Scale bar: 10 μm. I The colocalization analysis of F. n = 11–15. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns no significance