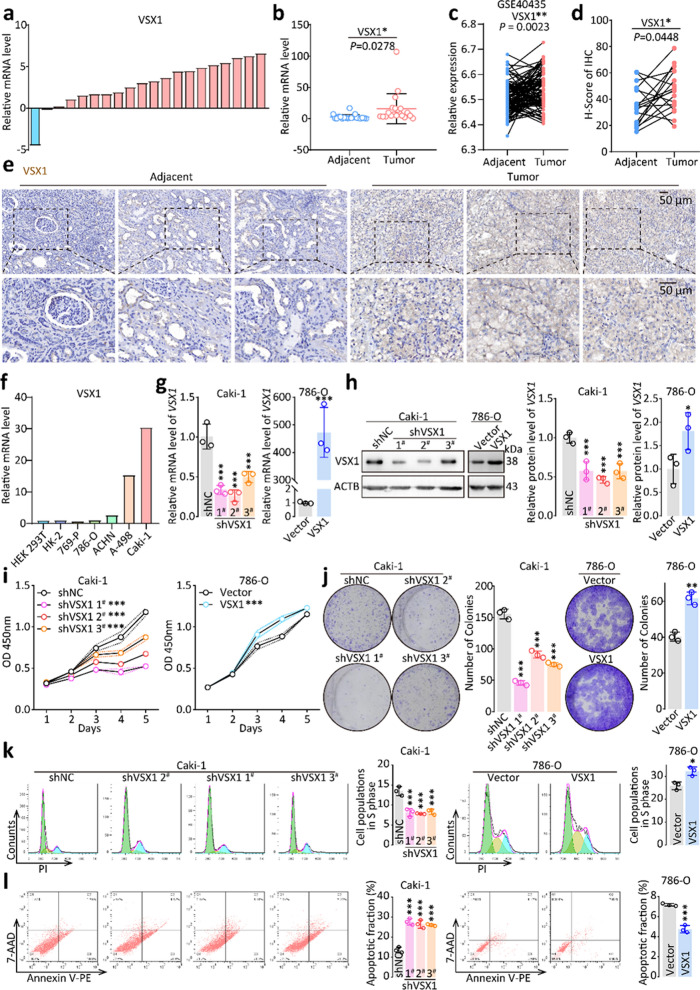
Fig. 3.
High VSX1 expression promoted cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in ccRCC. a − b qRT-PCR analyses of relative VSX1 mRNA expression in 20 pairs of human clinical ccRCC tissues. c VSX1 mRNA expression was validated based on the GSE40435 dataset. d − e Representative IHC staining of VSX1 in ccRCC tissues compared with paired adjacent noncancerous tissues and the staining scoring analysis. f VSX1 mRNA expression levels in a panel of human RCC cell lines were detected by qRT-PCR. g − h qRT-PCR and western blot verified the overexpression of VSX1 in 786-O cells and the knockdown of VSX1 in Caki-1 cells. i CCK-8 evaluated cell proliferation following VSX1 overexpression or knockdown. j VSX1 knockdown in Caki-1 cells inhibited colony formation, whereas the opposite results were reported in 786-O cells overexpressing VSX1. k − l Flow cytometry analyses showed that the knockdown of VSX1 expression in Caki-1 cells significantly increased the apoptosis rate and reduced cell populations in the S phase. Paired or unpaired Student’s t-tests and the one-way analysis of variance were used to assess the significance of differences. Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation.*P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001