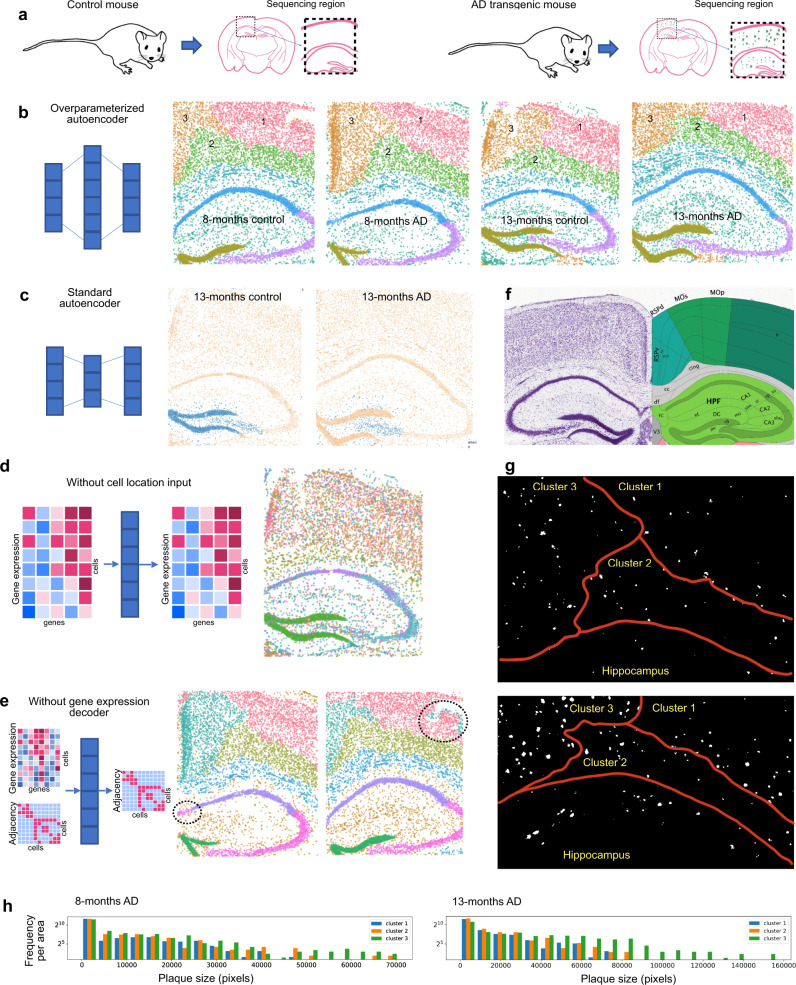
Fig. 2. Over-parameterized graph-based autoencoder model enables consistent and biologically meaningful annotation of spatial tissue regions across multiple samples and tissue sections.
a The STARmap PLUS dataset4 contains four mouse brain samples at 8 months and 13 months. Each time point consists of an AD mouse and a control mouse. Each tissue slice contains the cortex, corpus callosum, and hippocampus regions. b Clustering of the cells in the latent space learned by our over-parameterized autoencoder model leads to consistent spatial clusters across the four mouse samples. The latent dimension of this model is 6000 and a 20-nearest-neighbor graph was used to obtain the input cell adjacency matrix. Each dot is a cell plotted with its physical coordinates in the tissue and colored by the cluster memberships inferred in the latent space. c The use of standard (under-parameterized) autoencoder models leads to inconsistent spatial clusters across mouse samples: cells from the same cluster (blue) correspond to different regions in 13-months control (left) and 13-months AD (right) mice. The latent dimension of this model is 1024. d Clustering of the cells in the latent space by our autoencoder model without cell adjacencies as input cannot separate different spatial neighborhoods. e Clustering of the cells in the latent space by our autoencoder model without the gene expression decoder fails to separate the CA1 region from the CA2/CA3 region and produces inconsistent spatial regions in the cortex across mouse samples. f A reference slice from the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and Allen Reference Atlas - Mouse Brain45 showing approximately the same anatomical region as in the STARmap samples. Our model automatically segments the brain samples into continuous regions that correspond to the reference anatomical regions (cortex, hippocampus, dentate gyrus). g Binary images of amyloid plaque in the cortex of the 8-months AD sample (top) and 13-months AD sample (bottom) showing the spatial differences in plaque distribution in the three cortex clusters identified by our model. h Histograms of plaque size, measured in number of pixels, plotted for the three cortex regions, indicate larger plaque sizes in clusters 2 and 3 as compared to cluster 1. Frequency is normalized by the area of each cortex region.