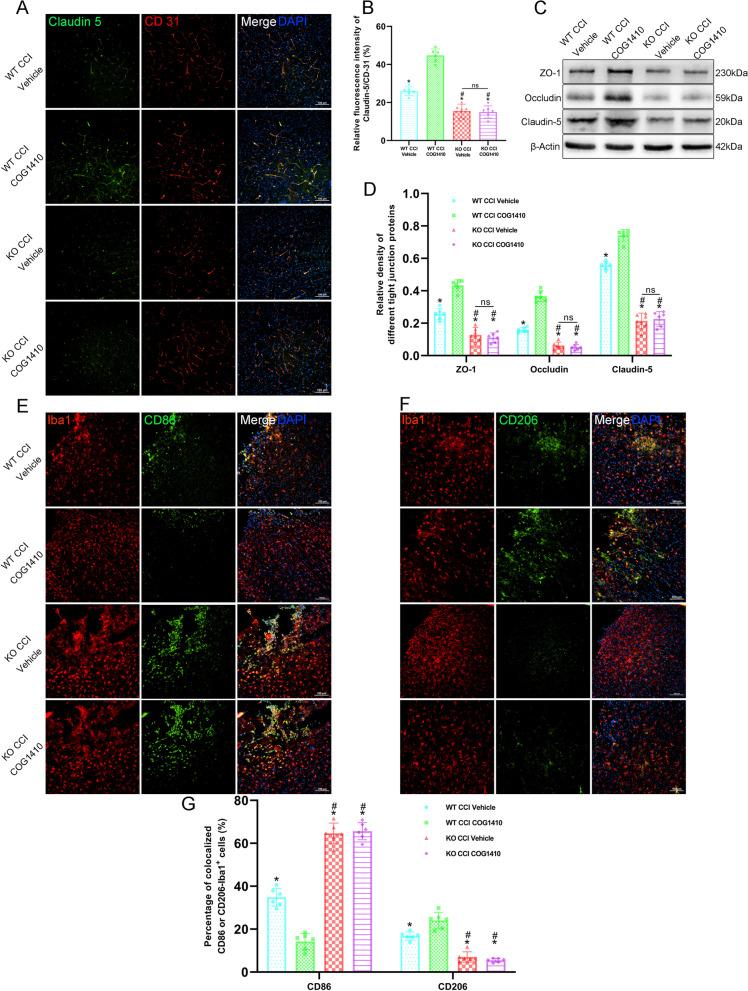
Fig. 10.
TREM2 depletion abolished the effects of COG1410 on vascular phenotypes and microglial states. A Representative images of Claudin-5 (green) and CD31 (red) surrounding the lesion sites at 3 d after CCI. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm. B Quantitative analysis of the relative Claudin-5 to CD31 fluorescence intensity in different groups. *p < 0.05 vs. WT CCI + COG1410; #p < 0.05 vs. WT CCI + Vehicle; ns p > 0.05 KO CCI + Vehicle vs. KO CCI + COG1410, n = 6 per group. C Representative Western blot bands of ZO-1, Occludin, Claudin-5, and β-Actin at the lesion sites after CCI. D Quantitative analysis of relative ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-5 density. *p < 0.05 vs. WT CCI + COG1410; #p < 0.05 vs. WT CCI + Vehicle; ns p > 0.05 KO CCI + Vehicle vs. KO CCI + COG1410, n = 6 per group. E Representative images of microglia (Iba1, red) and CD86-positive microglia (CD86, green) surrounding the lesion sites at 3 d after CCI. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm. F Representative images of microglia (Iba1, red) and CD206-positive microglia (CD206, green) surrounding the lesion sites at 3 d after CCI. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm. G Quantitative analysis of the percentage of colocalized CD86-Iba1+ cells and the percentage of colocalized CD206-Iba1+ cells in different groups at 3 d after CCI. *p < 0.05 vs. WT CCI + COG1410; #p < 0.05 vs. WT CCI + Vehicle; ns p > 0.05 KO CCI + Vehicle vs. KO CCI + COG1410, n = 6 per group