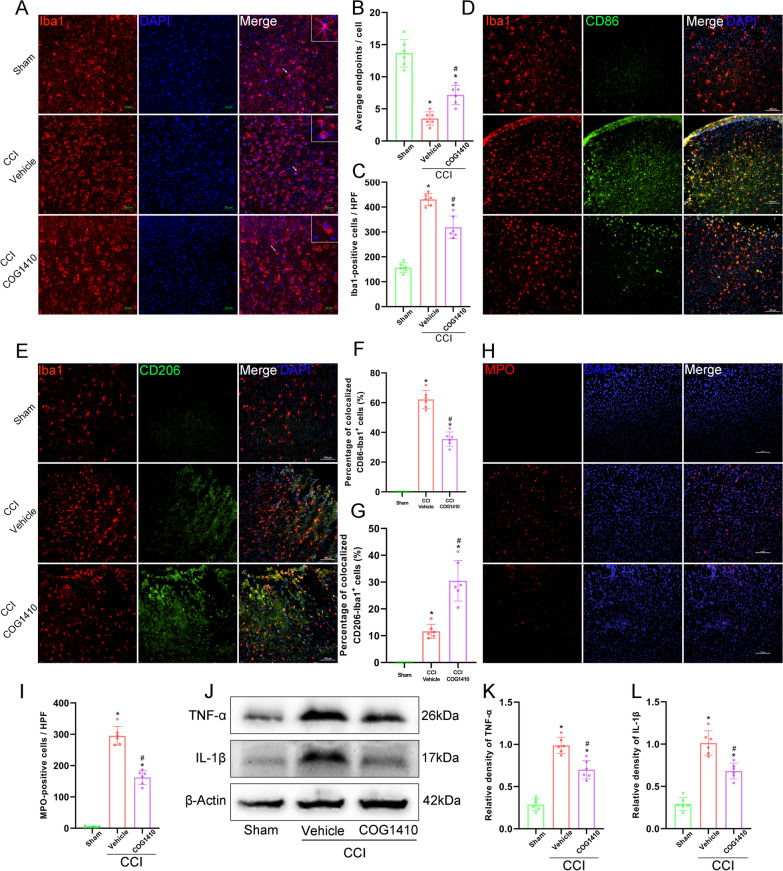
Fig. 5.
COG1410 treatment inhibited microglial activation, neutrophil infiltration, and the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β at 3 d after CCI. A Representative images of microglia (Iba1, red) surrounding the lesion sites. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. B, C Quantitative analysis of average endpoints of Iba1-positive cells (B) and number of Iba1-positive cells (C) per HPF. HPF, high power field. *p < 0.05 vs. Sham; #p < 0.05 vs. CCI + Vehicle, n = 6 per group. D Representative images of microglia (Iba1, red) and CD86-positive microglia (CD86, green) surrounding the lesion sites. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm. E Representative images of microglia (Iba1, red) and M2 microglia (CD206, green) surrounding the lesion sites. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm. F, G Quantitative analysis of the percentage of colocalized CD86-Iba1+ cells (F) and the percentage of colocalized CD206-Iba1+ cells (G). *p < 0.05 vs. Sham; #p < 0.05 vs. CCI + Vehicle, n = 6 per group. H Representative images of infiltrated neutrophils (MPO, red) surrounding the lesion sites. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm. I Quantitative analysis of MPO-positive cells per HPF. *p < 0.05 vs. Sham; #p < 0.05 vs. CCI + Vehicle, n = 6 per group. J Representative Western blot bands of TNF-α, IL-1β, and β-Actin. K, L Quantitative analysis of TNF-α (K) and IL-1β (L) density at the lesion sites after CCI. *p < 0.05 vs. Sham; #p < 0.05 vs. CCI + Vehicle, n = 6 per group