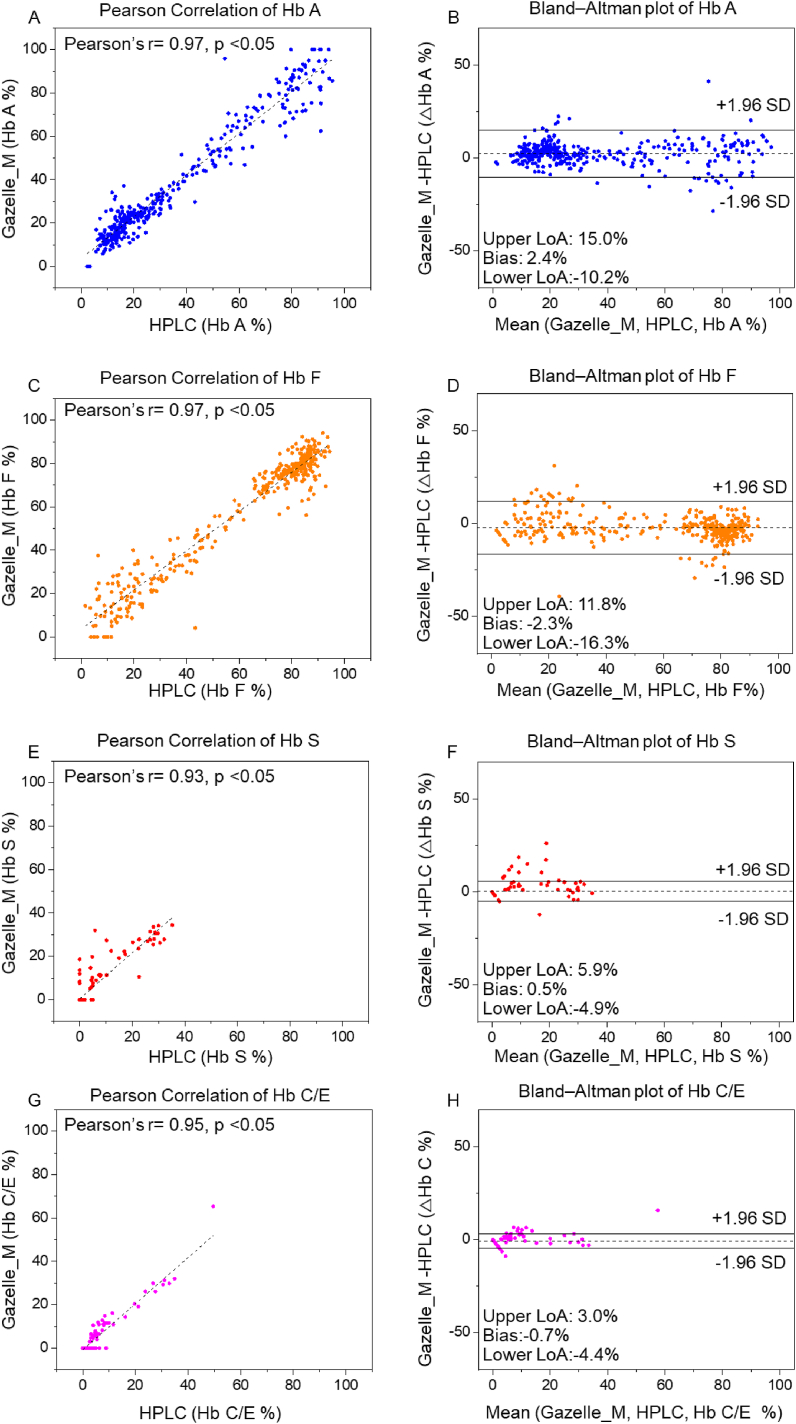
Figure 3.
Gazelle-Multispectral Hb variant identification and quantification in all test subjects. Pearson correlation (Column 1) and Bland-Altman analysis (Column 2) showed Gazelle-Multispectral identified and quantified Hb A (A&B, Pearson coefficient correlation (PCC) = 0.97, p < 0.05, Mean bias ±1.96 × Standard Deviation (SD) = 2.4% ± 12.6%), Hb F (C&D, PCC = 0.97, p < 0.05, Mean bias ±1.96SD = −2.3% ± −14.0%), Hb S (E&F, PCC = 0.93, p < 0.05, Mean bias ±1.96 SD = 0.5% ± 5.4%), and Hb C levels (G&H, PCC = 0.95, p < 0.05, Mean bias ±1.96SD = −0.7% ± 3.3%) agree with the ones reported by laboratory standard HPLC. In Column 2, the solid black lines indicate the mean biases and the dashed gray lines represent 95% limits of agreement. ∗: 365 ‘Valid’ tests out of 441 total tests were included in this correlation calculation. ‘Inconclusive’ tests did not generate a result that could be included in the correlation coefficient calculation [39, 40].