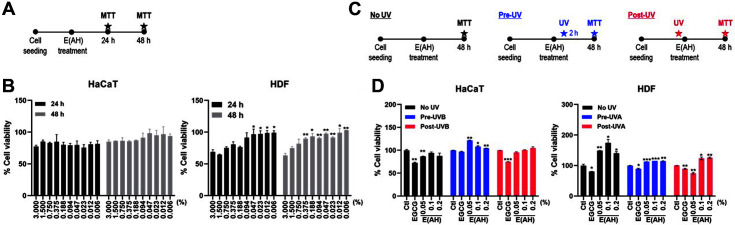
Fig. 3. E(AH) treatment does not cause cytotoxicity in UV-irradiated cultured human epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT) and human dermal fibroblasts (HDF).
(A) A schematic view of the MTT assay in E(AH)-treated HaCaT and HDF cells. (B) HaCaT and HDF cells were treated with various concentrations of E(AH). After incubation, MTT assay was performed to measure the cell viability of E(AH). All data were indicated as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (C) Schematic views of the MTT assay in UV-irradiated cells before and after treatment of the E(AH). (D) HaCaT and HDF cells were treated with either a control (Ctl), epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), or various concentrations of E(AH) before or after irradiation with UVA (3.0 J/cm2) or UVB (0.03 J/cm2). At 48 h, cell viability was examined by MTT assay. EGCG was used as a positive control for the following experiments. All data were indicated as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. Ctl-treated cells.