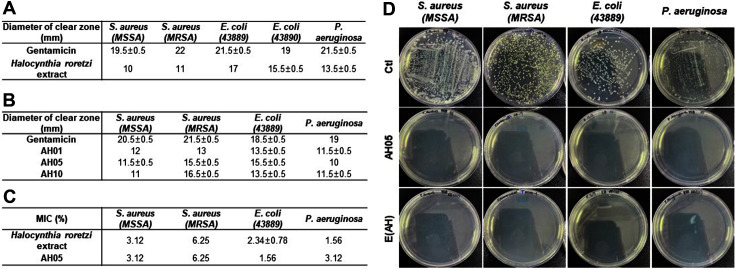
Fig. 6. AH and E(AH) show antibacterial activities against multiple bacterial strains.
(A) For paper disc diffusion assay S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa were cultured overnight. Filter paper discs (8 mm) were soaked in Halocynthia roretzi extracts and placed on the plate and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Then, the diameter of the clear zone was measured. (B) A paper disc diffusion assay was performed to examine the antibacterial effect of AH compounds against S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa. (C) Bacteria in the exponential growth phase were inoculated in Halocynthia roretzi extracts or AH compoundcontaining media broth. After overnight incubation, absorbance at 600 nm was measured. (D) AH05 compound or E(AH) were added to bacterial suspensions of S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa. Next day, bacterial suspensions were serially diluted and plated onto the LB or TSB plate to measure the colony-forming units. All data were indicated as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.