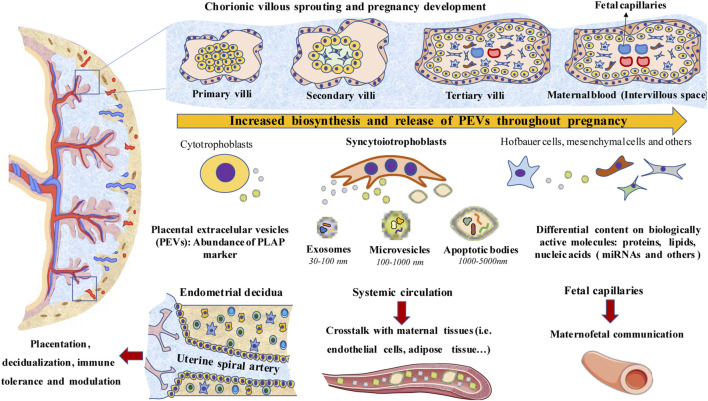
FIGURE 1.
A general overview of PEVs. Biosynthesis and release of PEVs increase as pregnancy progresses along with the development of the placental structures. Syncytiotrophoblasts, which are in contact with maternal blood (Intervillous space), are a major source of PEVs, although cytotrophoblast, Hofbauer cells, mesenchymal cells, extravillous trophoblasts and others also produce them. PEVs are essential for the interplay between the placenta and endometrial decidua, modulating both the placentation and decidualization processes. PEVs also modulate the immune system, the inflammatory response and immune tolerance. PEVs reach systemic circulation or enter through fetal capillaries into the fetal circulation, playing a key role in the crosstalk between the placenta with maternal and fetal tissues.