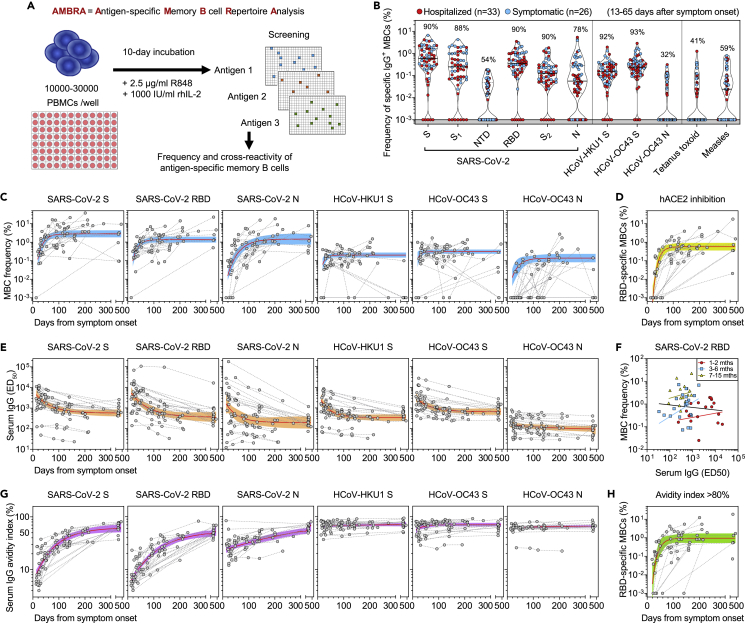
Figure 1.
Early response, RBD immunodominance, kinetics, and affinity maturation of memory B cells primed by Wuhan-Hu-1 SARS-CoV-2
(A) Scheme of the AMBRA method used in this study. PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells. R848, agonist of Toll-like receptors 7 and 8. rhIL2, recombinant human interleukin-2.
(B) Frequency of SARS-CoV-2-specific MBCs isolated between 13 and 65 days after symptom onset from n = 59 donors (33 hospitalized, red, and 26 symptomatic, blue) after the analysis of 5664 MBC cultures. Shown is the reactivity to antigens of SARS-CoV-2 and other betacoronaviruses (HCoV-HKU1 and HCoV-OC43): Spike (S), S1 domain, N-terminal domain (NTD), receptor-binding domain (RBD), S2 domain, Nucleoprotein (N). Reactivities to Tetanus toxoid and to Measles virus (lysate) are included as controls. Median and quartiles are shown as plain and dotted lines, respectively. Percentages of donors with detectable specific MBCs are indicated above each set of data.
(C) Frequency of MBCs specific for SARS-CoV-2 S, RBD and N, HCoV-HKU1 S, HCoV-OC43 S and N from n = 23 donors followed-up up to 469 days after symptom onset. Frequencies were obtained from the analysis of 6336 MBC cultures (66 samples, minimum 2 samples per donor). Black dotted lines connect samples from the same donor. A one-phase association kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample. The area within 95% confidence bands is shown in blue.
(D) Frequency of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific MBC-producing antibodies showing the inhibition of RBD binding to ACE2 from n = 23 donors. A one-phase association kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample and the area within 95% confidence bands is shown in yellow.
(E) Serum IgG ED50 titers to SARS-CoV-2 S, RBD and N, HCoV-HKU1 S, HCoV-OC43 S and N of samples collected from 29 donors analyzed up to 469 days after symptom onset. A one-phase decay kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample and the area within 95% confidence bands is shown in orange.
(F) Correlation analysis between frequency of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific MBCs and serum RBD-specific IgG titers of n = 56 samples from n = 18 donors collected at different time points. All samples (black line): Spearman r = −0.102 (95% confidence interval −0.363 to 0.173; non-significant p = 0.45). Samples at 1-2 months (n = 18, red line): Spearman r = 0.112 (95% confidence interval −0.387 to 0.561; non-significant p = 0.66). Samples at 3-6 months (n = 23, blue line): Spearman r = 0.214 (95% confidence interval −0.229 to 0.584; non-significant p = 0.33). Samples at 7-15 months (n = 15, yellow line): Spearman r = 0.221 (95% confidence interval −0.343 to 0.668; non-significant p = 0.43).
(G) Serum IgG avidity indexes to SARS-CoV-2 S, RBD and N, HCoV-HKU1 S, HCoV-OC43 S and N of samples collected from 29 donors analyzed up to 469 days after symptom onset. A one-phase association kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample and the area within 95% confidence bands is shown in violet.
(H) Frequency of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific B cells with an avidity index greater than 80%. A one-phase association kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample and the area within 95% confidence bands is shown in green. See also Figure S1 and Table S1.