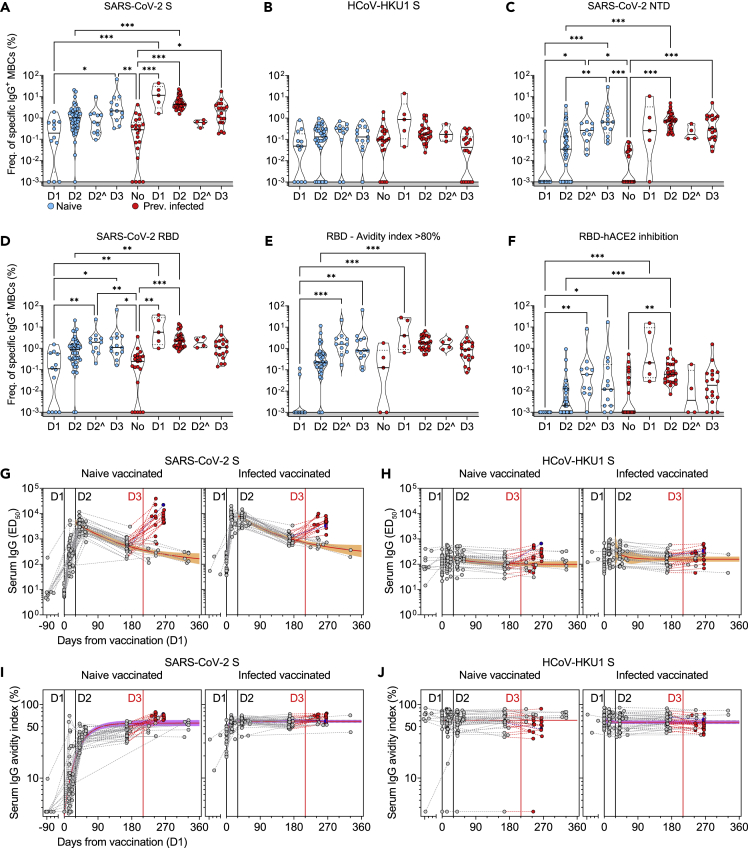
Figure 2.
Characterization of vaccine-induced MBC- and serum-derived antibody response in naive and SARS-CoV-2 immune donors
(A-D) Frequency of MBCs specific for SARS-CoV-2 S (A), HCoV-HKU1 S (B), SARS-CoV-2 NTD (C) and RBD (D) of n = 12, 45, and 13 naive donors and 5, 31, and 18 previously infected donors 10-35 days after the first (D1), the second (D2) and the third dose (D3) of Pfizer/BioNtech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine, respectively. Shown are also 11 naive and 4 immune donors whose MBCs were isolated 125-293 days after the second dose (D2ˆ). Median frequencies are compared withing donor groups and between respective vaccine doses as well as to a group of n = 21 convalescent donors at 18-30 days after symptom onset. Significant differences are indicated as ∗∗∗ (p <0.001); ∗∗ (p < 0.002), ∗ (p < 0.033).
(E) Frequency of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific MBCs with an avidity index greater than 80%.
(F) Frequency of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific MBCs inhibiting binding of RBD to ACE2.
(G and H) Serum IgG ED50 titers to SARS-CoV-2 S (G) and HCoV-HKU1 S (H) of samples collected from n = 47 naive (left) and 32 immune donors (right) 10-35 days after the first (D1), the second (D2) and the third dose (D3) of Pfizer/BioNtech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine, respectively. A one-phase decay kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample and the area within 95% confidence bands is shown in orange. 37 samples collected from individuals who received a third dose (red) or had a second SARS-CoV-2 infection (blue) were excluded from the decay analysis.
(I and J) Serum IgG avidity indexes to SARS-CoV-2 S (I) and HCoV-HKU1 S (J) of the same samples shown in panels G-H. A one-phase association kinetics model (red line) was calculated from all the non-null values of each sample and the area within 95% confidence bands is shown in violet. See also Figure S2 and Table S1.