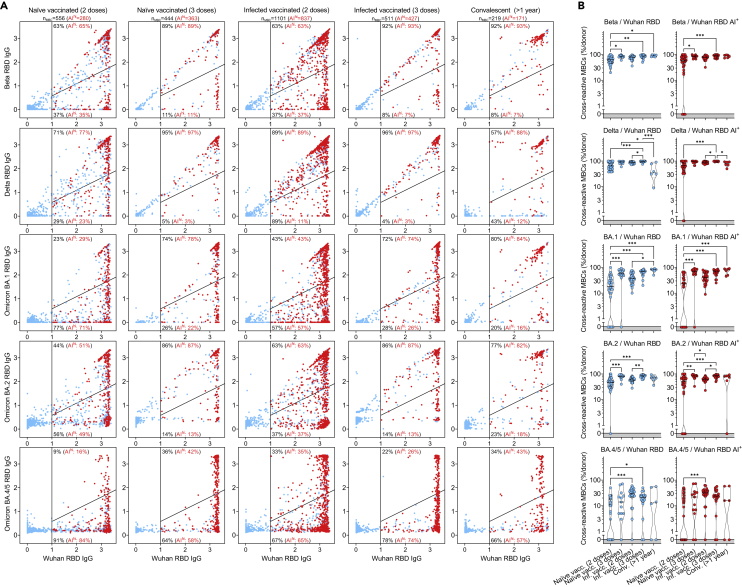
Figure 6.
Resilience to viral escape of VOC by high-avidity MBCs primed by SARS-CoV-2 infection and/or vaccination
(A) Cumulative MBC cross-reactivity between RBD from Wuhan-Hu-1 SARS-CoV-2 and Beta, Delta, Omicron BA.1, BA.2, and BA.4/5 VOC. Shown are average OD values as measured by ELISA with blank subtracted from n = 2 replicates of 2976, 1248, 2304, 1728, and 576 MBC cultures analyzed from 31 to 13 naive donors, 24 and 18 infected donors after receiving two and three vaccine doses and from 6 convalescent donors at 376-469 days from symptom onset. RBD-specific MBCs showing high avidity index (AI>80%) are shown in red. Numbers of total and high-avidity RBD-specific MBCs are indicated in the top-left quadrants. Cumulative fractions of total and high-avidity RBD-specific MBCs maintaining or losing binding to the VOC RBD are indicated as a percentage in the top-right and bottom-right quadrants.
(B) Individual fractions of total (left) and high-avidity (right) SARS-CoV-2 RBD-cross-reactive MBCs that maintain binding with the RBDs of different VOC in 31 and 13 naive donors, 24 and 18 infected vaccinated donors after receiving two and three vaccine doses and in 6 convalescent donors at 376-469 days from symptom onset. Significant differences are indicated as ∗∗∗ (p-value < 0.001); ∗∗ (p < 0.002), ∗ (p < 0.033). See also Figure S6.