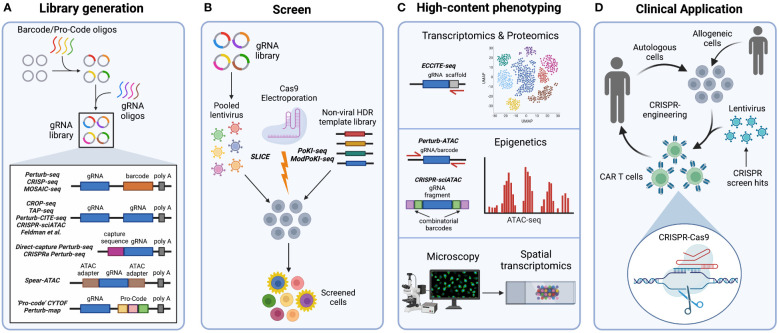
Figure 2.
Steps in high-content CRISPR screening. (A) For systems that use barcodes or Pro-Codes, these oligonucleotides are first cloned into a viral vector, followed by guide RNA (gRNA) oligonucleotides to create unique paired gRNA-barcode/Pro-Code constructs that are recognized during sequencing. Meanwhile, systems that use the non-barcoded CROP-seq vector contain gRNA sequences that are directly sequenced without the need for barcodes. Furthermore, Direct-capture Perturb-seq and CRISPRa Perturb-seq vectors contain capture sequences within gRNA scaffold regions that are recognized during sequencing. In Spear-ATAC vectors, adapters used in ATAC-seq flank the gRNA sequence for direct amplification from the genomic DNA during ATAC-seq. (B) Introduction of the CRISPR-Cas9 system into cells for pooled content-rich screening can occur in multiple ways. Pooled vectors can be used to generate lentivirus, which then transduce and integrate into target cell genomes in the presence of Cas9. If Cas9 is not simultaneously transduced or expressed by target cells, SLICE (sgRNA lentiviral infection with Cas9 protein or electroporation) may be employed to introduce Cas9. Furthermore, the PoKI-seq system can be used for pooled knockin screening by simultaneously electroporating a gRNA : Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex with a non-viral barcoded homology directed repair template library. (C) Phenotypic readouts of high-content CRISPR screens include transcriptomic, proteomic, epigenetic, and microscopy data. ECCITE-seq specifically adds gRNA scaffold-targeted primers to detect the gRNA during scRNA-seq. Perturb-ATAC uses pooled primers to target flanking regions of the barcode or gRNA during ATAC-seq. Meanwhile, in the CRISPR-sciATAC system, gRNA and ATAC fragments are labeled with combinatorial barcodes for detection during ATAC-seq. Finally, optical readouts include imaging followed by spatial transcriptomics. (D) The CRISPR-Cas9 system is a significant tool for clinical advancement. CRISPR-Cas9 editing may be used to target genes identified by immune cell CRISPR screens controlling antitumor functions. Autologous or allogeneic engineered cells, such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, may then be adoptively transferred into patients.