Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Experimental design, cell population consistency, and pathways analysis of the scRNA-seq experiment conducted on hippocampal BEC isolated from LPS and CLU treated mice.
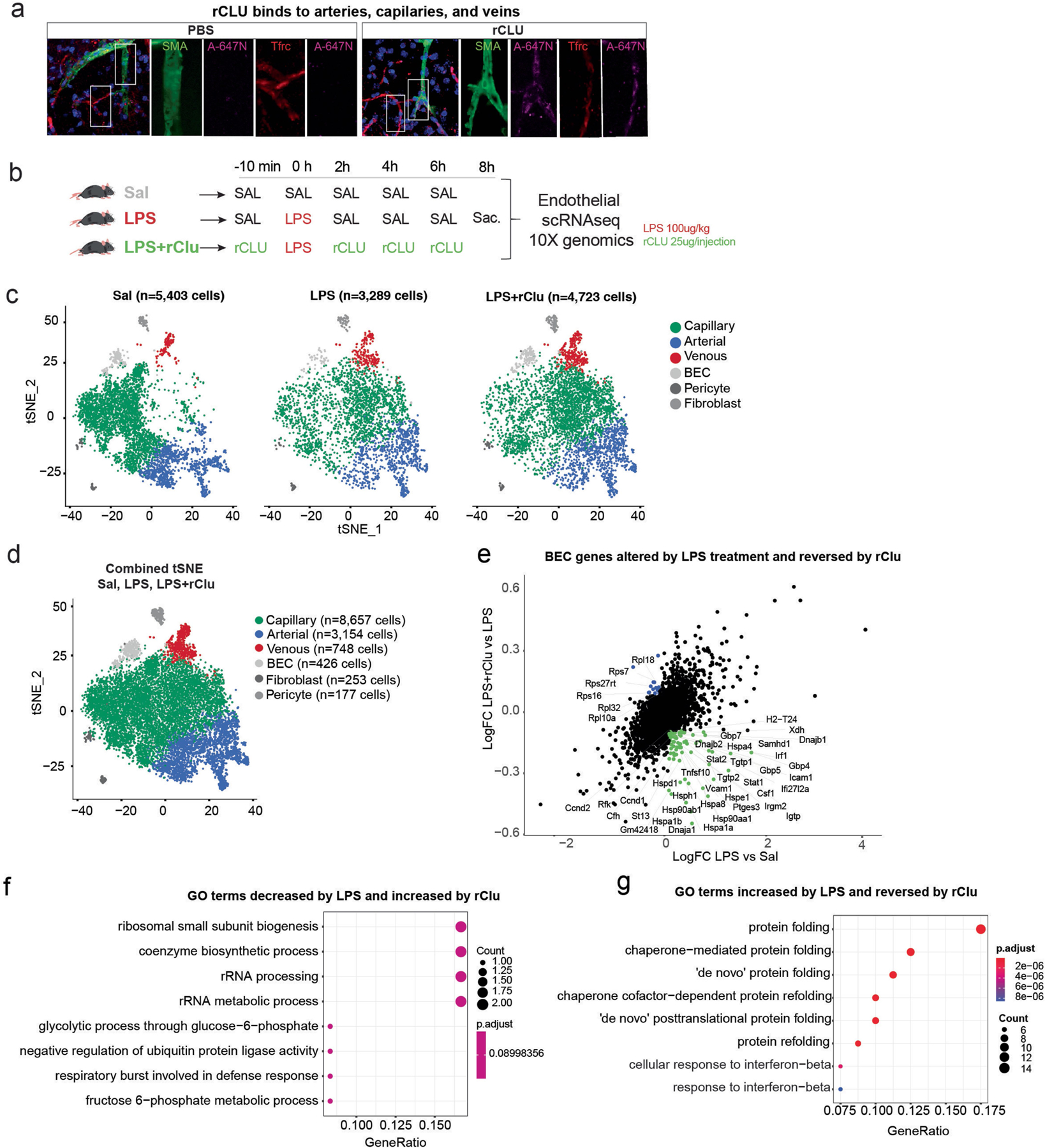
a, Confocal representative images show peripherally injected rCLU tagged with Atto-647N or control PBS containing Atto-647N colocalized with cells of the cerebrovasculature, arteries (SMA), capillaries and veins (Tfrc). Scale bars, 10 μm. b, Schematic depicting the experimental paradigm followed for the injections of the three groups. 3- to 4-month-old male mice received Saline only injections (Sal), LPS plus saline treatments (LPS), or LPS plus recombinant CLU (LPS+Clu). BECs were isolated from n = 4–5 per group. c, tSNE plots showing the cellular proportions, numbers, and distributions in the three experimental groups (Sal, LPS, LPS+Clu). d, tSNE plots show distribution of BECs among arterial, capillary, and venous cells by group. Combined tSNE plot for BECs sorted from 3- to 4-month-old male mice (n = 4–5 mice per group) treated with Saline, LPS, and LPS+CLU. (Cells labelled as BEC are of low quality and were excluded from differential expression analysis.). e, Scatter plots show a list of selected genes altered in BECs (arterial, capillary, and venous) by acute inflammation (LPS) and reversed by CLU treatment. Coloured genes represent genes that pass the cutoff fold change of 1.1. Green: Genes increased by inflammation and reversed by CLU. Blue: Genes reduced by inflammation and reversed by CLU. (Log FC: natural logarithm of fold change). f-g, Dotplot showing Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Processes terms for BEC genes (Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment test, FDR < 0.05) that decrease or increase by LPS treatment and are reversed by CLU. Genes were selected based on the cutoff fold change of 1.1. The images in b were generated using MediaLab (https://medialab.biochem.wisc.edu/clip-art/).
