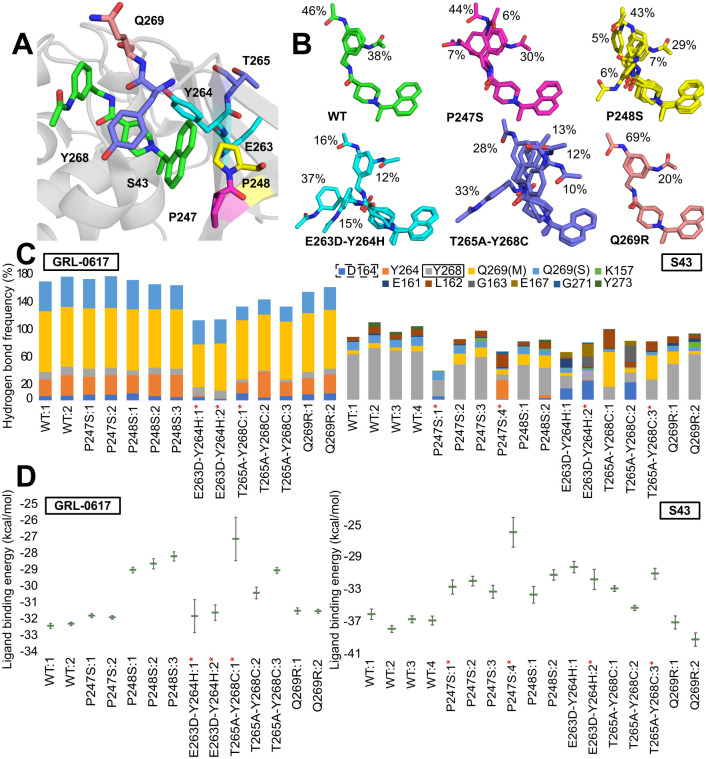
Fig 3. Selected variants found in PLpro.
(A) Location of amino acids subject to mutation relative to the ligand (S43) binding site (based on PDB ID: 7d7t). (B) Representative S43 conformations bound to PLpro. Calculations are based on frames sampled every 100 ps from joint Molecular Dynamics trajectories. Conformations found in less than 5% of the frames are not shown for clarity. (C) Frequency of protein-ligand hydrogen bonds in different trajectories. Left: GRL-0617, right: S43. Calculations are based on frames sampled every 100 ps from Molecular Dynamics trajectories. Dashed rectangle points to the amino acid interacting via hydrogen bond with GRL-0617 in the crystal structure (PDB ID: 7jrn), the one with solid line with S43 (PDB ID: 7d7t). In the case of Q269 the ligand can bind to either its main chain (M) or side chain (S). The red asterisk indicates the trajectories in which the ligand dissociated from the binding site. (D) Ligands MMGBSA binding energy (kcal/mol) to PLpro. Left: GRL-0617, right: S43. Calculations are based on frames sampled every 100 ps from Molecular Dynamics trajectories—the averages and standard errors are shown. The trajectories in which the ligand dissociated from the binding site are marked with red asterisk.