Figure 2. OTS964 binds CDK11 in an active-like conformation.
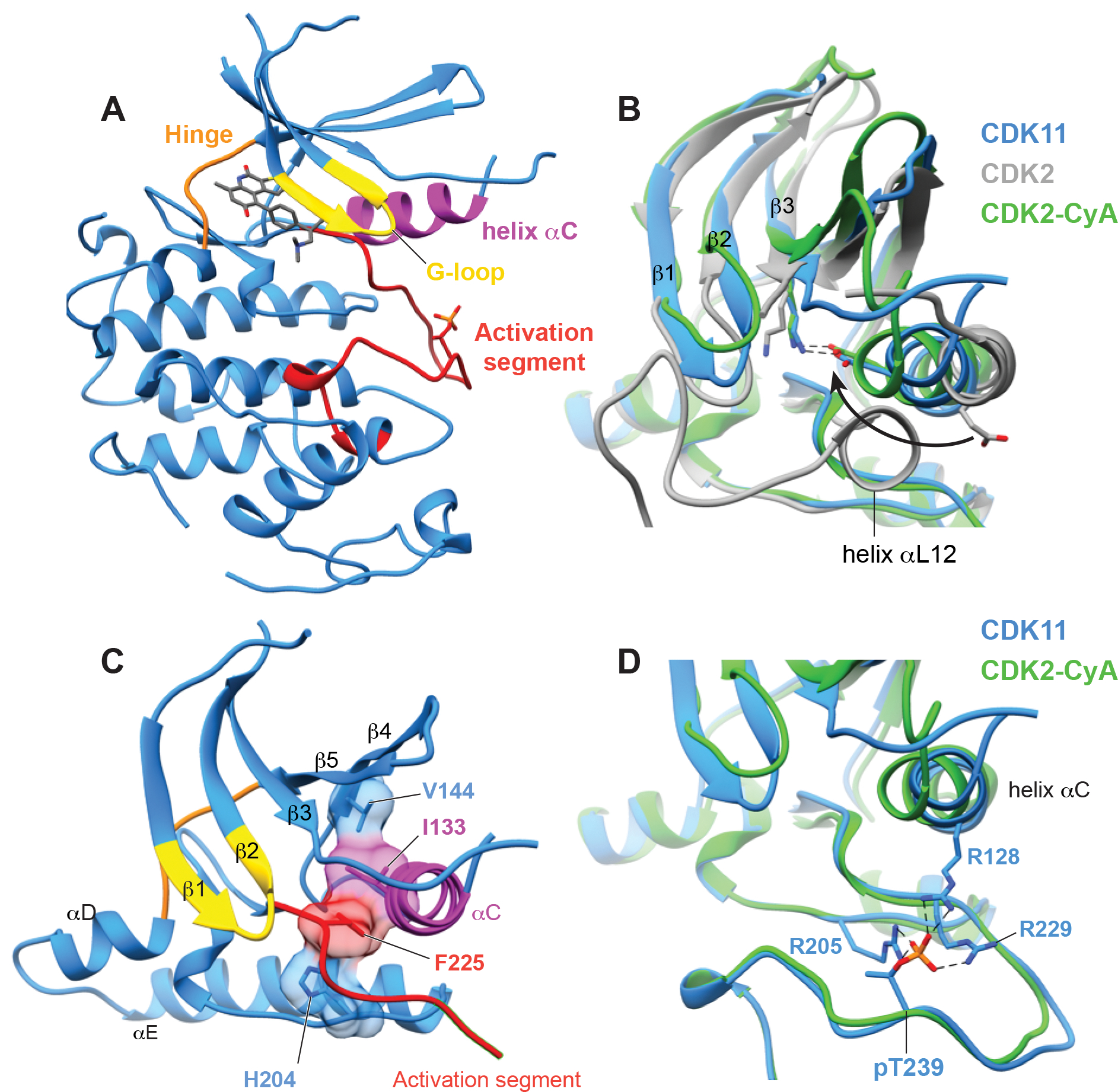
(A) The overall structure of CDK11 with OTS964 bound in the active site, highlighting the position of important kinase substructures the G-loop (yellow), helix αC (magenta), the hinge between the N and C lobes (orange), and the activation segment (red).
(B) View of helix αC of CDK11 comparing the overall position of the helix and direction of conserved glutamate (CDK11 E129, CDK2 E51) to structures of CDK2-cyclin A (PDB 1QMZ, Brown et al., 1999) and CDK2 without a cyclin (PDB 1HCK, Schulze-Gahmen et al., 1996).
(C) View of the R-spine residues of CDK11 which are aligned within the kinase domain.
(D) View of on the conformation of the phosphorylated activation segment of CDK11 compared to the phosphorylated activation segment CDK2 and showing the position of phospho-Thr229 which is coordinated by indicated arginine residues.
