Figure 2. ctDNA profiling enhances the detection of somatic variants at the time of neuroblastoma diagnosis or relapse.
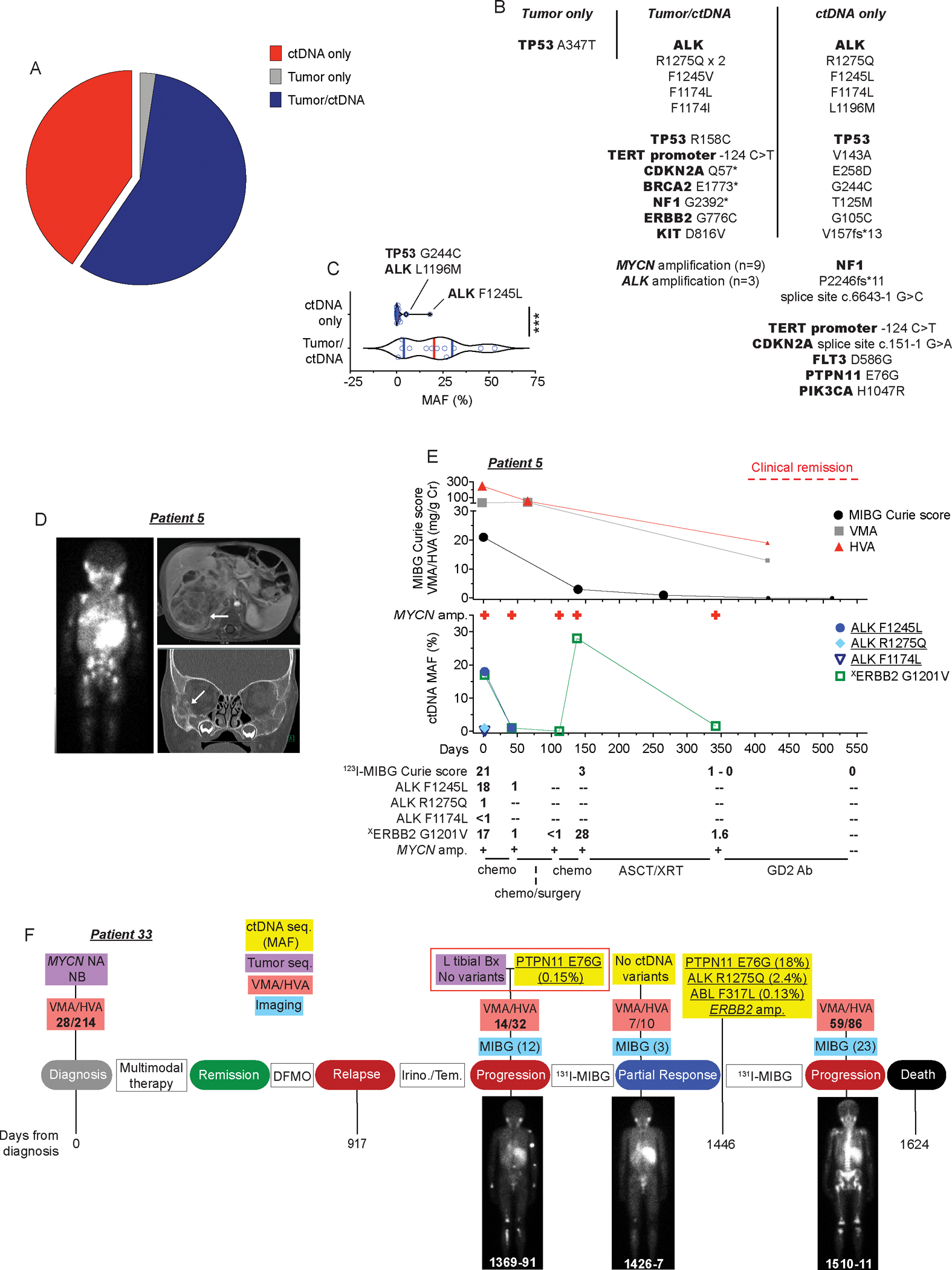
(A) Plot showing concordance between tumor and ctDNA sequencing identified variants from temporally paired samples at the time of diagnosis or relapse (n=28 patients).
(B) Description of gene variants summarized in A.
(C) MAF of gene variants shown in B stratified by those identified in ctDNA only versus those found in both tumor and ctDNA.
(D) 123I-MIBG scan (left), MRI (top right), and CT scan (bottom right) of 1-year-old male (patient 5) who presented with widely metastatic neuroblastoma. White areas of MIBG scan (left) and white arrows on MRI and CT images indicate areas of disease.
(E) Serial ctDNA and disease evaluation correlation plot for patient 5 in D showing relationship between 123I-MIBG Curie scores, a semi-quantitative measure of tumor burden, urine catecholamine levels (VMA/HVA in mg/g Cr; top) and ctDNA profiling data (middle). Larger symbols in plot represent abnormal values. Numbers in bottom table denote MAFs and MIBG Curie scores. General treatment schema shown at bottom of plot.
(F) Serial ctDNA and disease evaluation correlation timeline for patient 33. Images are representative 123I-MIBG images with Curie scores noted in parentheses. VMA/HVA quantification (mg/g Cr) is indicated (bolded values represent abnormal values) and days from neuroblastoma diagnosis is noted on the bottom of plot.
Chemo, chemotherapy; ASCT, autologous stem-cell transplant; XRT, radiation therapy; NB, neuroblastoma; Seq., sequencing; NA, not-amplified; Bx, biopsy; GD2 Ab, GD2-targeting chimeric monoclonal antibody dinutuximab; DFMO, difluoromethylornithine, an irreversible inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) used in maintenance neuroblastoma therapy; Irino./Tem., irinotecan/temozolomide, a chemotherapeutic regimen used commonly for relapsed neuroblastoma therapy; 131I-MIBG, 131I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine, a targeted radiotherapeutic used to treat neuroblastoma.
Underlined variants in E and F denote those unique to ctDNA and (X) denotes variant of unknown significance.***p < 0.0001.
