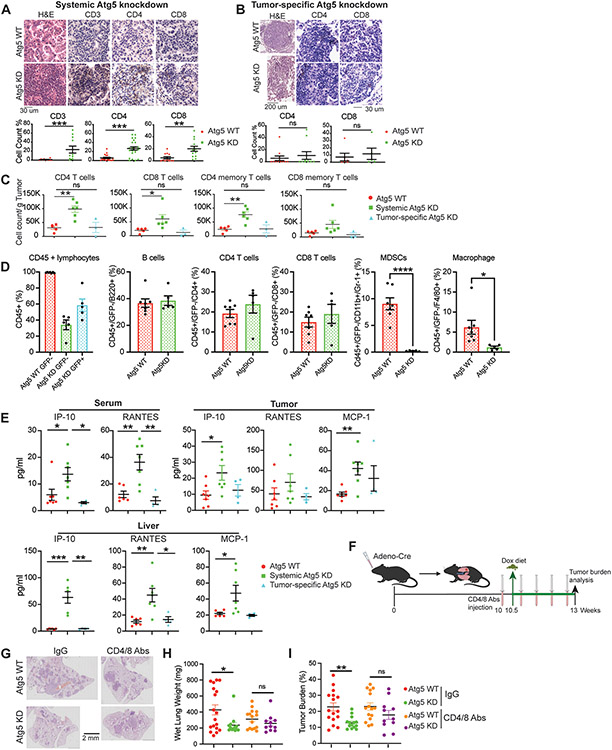
Figure 5. Systemic autophagy suppresses T cell-mediated tumor killing for KP lung tumor growth.
A. Representative H&E staining, IHC images and quantifications of CD3, CD4 and CD8 T cells in lung tumors of WT and systemic Atg5 knockdown mice.
B. Representative H&E staining, IHC images and quantifications of CD4 and CD8 T cells in lung tumors of WT and tumor-specific Atg5 knockdown mice.
C. CD4, CD8, CD4 memory and CD8 memory T cells in KP lung tumors of WT, systemic Atg5 knockdown, and tumor-specific Atg5 knockdown mice examined via multiplex immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometry sorting at four weeks post Dox treatment.
D. Circulating blood immunoprofiling of WT and systemic Atg5 knockdown mice examined via multiplex immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometry sorting at four weeks post Dox treatment.
E. Serum, tumor and liver cytokine and chemokine profiling of WT, systemic Atg5 knockdown, and tumor-specific Atg5 knockdown mice at four weeks post Dox treatment.
F. Scheme of co-depletion of CD4 and CD8 T cells to assess the role of systemic autophagy in modulating immune response for established KP lung tumor growth.
G. Representative histology (H&E staining) of scanned lung sections of WT and systemic Atg5 knockdown mice without or with CD4/CD8 T cell depletion.
H. Graph of wet lung weight of WT and systemic Atg5 knockdown mice without or with CD4/CD8 T cell depletion.
I. Quantification of tumor burden of WT and systemic Atg5 knockdown mice without or with CD4/CD8 T cell depletion from (F).
Data are mean± s.e.m. n.s., P>0.05; * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.005