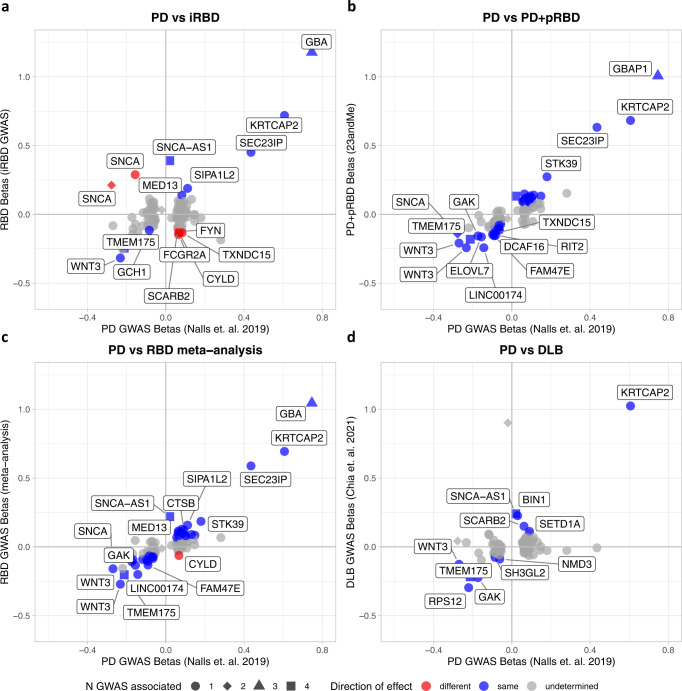
Fig. 5. Beta-beta plots comparing synucleinopathy GWAS summary statistics to the latest PD GWAS.
PD Parkinson’s disease, RBD REM sleep behavior disorder, GWAS genome-wide association study, pRBD probable RBD, DLB dementia with Lewy bodies. We compare significance and direction of PD GWAS-nominated loci to this study’s summary statistics for iRBD (a), PD+pRBD (b), the meta-analysis (c), and in the previously published DLB summary statistics (d). Colored points indicate variants with the same (blue) or opposite (red) direction of effect in both studies, with a nominally significant p-value (p < 0.05) in their respective genome-wide association studies (two-sided p-value derived from logistic regression across the genome). All test statistics for each cohort can be found in Supplementary Table 5. Gray points are those with undetermined direction (p > 0.05 and confidence intervals cross 0). The shapes of the points indicate the number of synucleinopathy GWAS where the locus reaches GWAS significance (counting PD, PD age at onset, DLB, and this RBD meta-analysis). Gene names indicate the closest gene to the represented variant.