Fig. 7. Key GWAS-significant loci across three synucleinopathies.
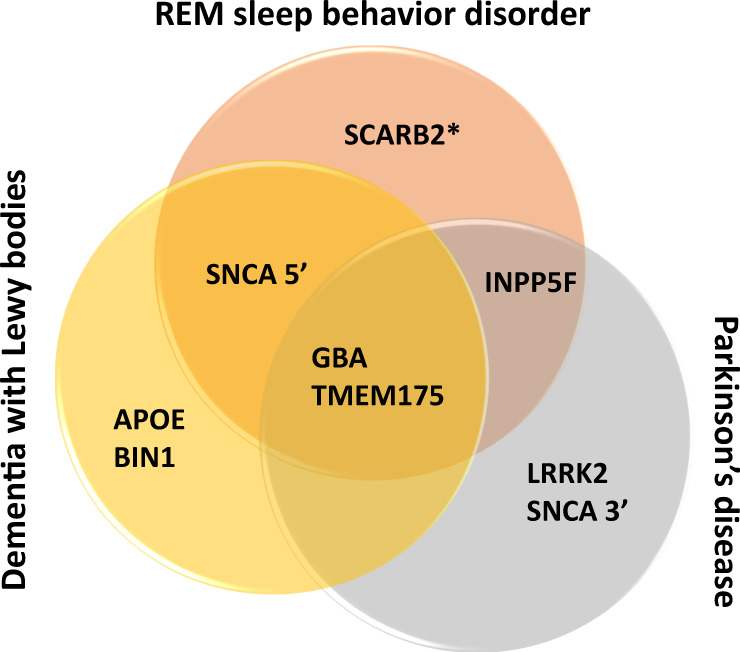
It has been shown that the genetic risk for PD and DLB do not overlap completely, and we show that the same is true for RBD and the other two synucleinopathies. Here, we demonstrate key genetic risk loci for the three synucleinopathies. Only GBA and TMEM175 are shared between all three, both of which play a role in the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. SNCA plays a role in PD, DLB, and RBD risk, yet the strongest risk locus for PD is at the 3’ end of the gene while RBD and DLB share a risk locus at the 5’ end. Similarly, SCARB2 is a risk factor for PD as well as RBD, however, the RBD locus is independent of the variant identified for PD risk (as indicated by the asterisk in the figure).
