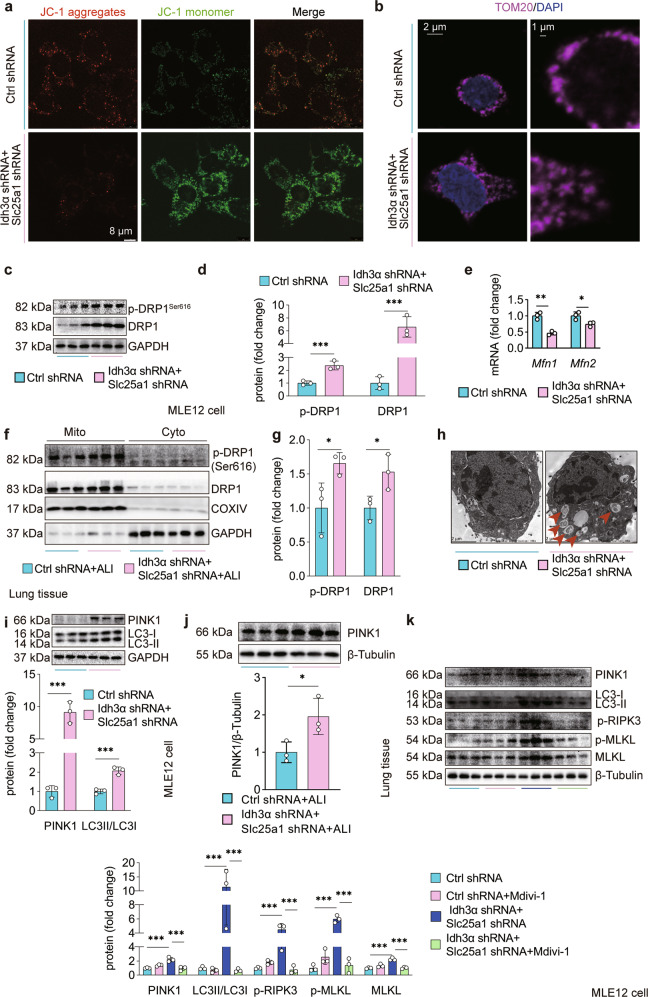
Fig. 6. Citratemt accumulation induces excessive mitophagy via DRP1.
a MMP was assessed by confocal laser scanning microscopy using the dye JC-1. b Confocal immunofluorescence staining of TOM20 was performed to visualize mitochondrial fission induced by citratemt accumulation. c Mfn1 and Mfn2 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR. d–e The total and Ser616 phosphorylated forms of DRP1 were measured by immunoblotting. f, g Adenovirus vectors (1 × 108 PFU/20 g) to specifically silence Slc25a1 and Idh3α in AECs were injected 10 days prior to tracheal instillation of LPS (2.5 mg/kg), and the mice were sacrificed 12 h after LPS administration. Mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions were prepared. Silencing slc25a1 and Idh3α in AECs increased total and DRP1 protein in mitochondria (n = 3). h Autophagosome formation in mitochondria was detected by TEM. i, j The protein expression of PINK1 and LC3II/LC3I was measured by immunoblotting (n = 3). To observe the effects of DRP1 on mitophagy and necroptosis, MLE12 cells were treated with the DRP1-specific inhibitor Mdivi-1 (10 μM) for 1 h before lentiviral vector restimulation. k Mitophagy-related proteins (PINK1 and LC3II/LC3I) and necroptosis-related proteins (p-RIPK3, MLKL, and p-MLKL) were detected by immunoblotting (n = 3). The data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.